A November 15, 2013 article by Alice Truong about Frontiers for Young Minds (for Fast Company), profiles a new journal meant to be read by children and edited and peer-reviewed by children. Let’s start with an excerpt from the Truong article as an introduction to the Frontiers for Young Minds journal (Note: Links have been removed),
Frontiers for Young Minds is made up of editors ages 8 to 18 who learn the ropes of peer review from working scientists. With 18 young minds and 38 adult authors and associate editors lending their expertise, the journal–an offshoot of the academic research network Frontiers …
With a mission to engage a budding generation of scientists, UC [University of California at] Berkeley professor Robert Knight created the kid-friendly version of Frontiers and serves as its editor-in-chief. The young editors review and approve submissions, which are written so kids can understand them–“clearly, concisely and with enthusiasm!” the guidelines suggest. Many of the scientists who provide guidance are academics, hailing from Harvard to Rio de Janeiro’s D’Or Institute for Research and Education. The pieces are peer reviewed by one of the young editors, but to protect their identities only their first names are published along with the authors’ names.
Great idea and bravo to all involved in the project! Here’s an excerpt from the Frontiers for Young Minds About webpage,
Areas in Development now include:
- The Brain and Friends (social neuroscience)
- The Brain and Fun (emotion)
- The Brain and Magic (perception, sensation)
- The Brain and Allowances (neuroeconomics)
- The Brain and School (attention, decision making)
- The Brain and Sports (motor control, action)
- The Brain and Life (memory)
- The Brain and Talking/Texting (language)
- The Brain and Growing (neurodevelopment)
- The Brain and Math (neural organization of math, computational neuroscience)
- The Brain and Health (neurology, psychiatry)
- The Brain and Robots (brain machine interface)
- The Brain and Music (music!)
- The Brain and Light (optogenetics)
- The Brain and Gaming (Fun, Action, Learning)
- The Brain and Reading
- The Brain and Pain
- The Brain and Tools (basis of brain measurements)
- The Brain and History (the story of brain research)
- The Brain and Drugs (drugs)
- The Brain and Sleep
I believe the unofficial title for this online journal is Frontiers (in Neuroscience) for Young Minds. I guess they were trying to make the title less cumbersome which, unfortunately, results in a bit of confusion.
At any rate, there’s a quite a range of young minds at work as editors and reviewers, from the Editorial Team’s webpage,
Sacha
14 years old
Amsterdam, Netherlands
When I was just a few weeks old, we moved to Bennekom, a small town close to Arnhem (“a bridge too far”). I am now 14 and follow the bilingual stream in secondary school, receiving lessons in English and Dutch. I hope to do the International Bacquelaurate before I leave school. In my spare time, I like to play football and hang out with my mates. Doing this editing interested me for three reasons: I really wanted to understand more about my dad’s work; I like the idea of this journal that helps us understand what our parents do; and I also like the idea of being an editor!
Abby
11 years old
Israel
I currently live in Israel, but I lived in NYC and I loved it. I like wall climbing, dancing, watching TV, scuba diving, and I love learning new things about how our world works. Oh, I also love the Weird-but-True books. You should try reading them too.
Caleb
14 years old
Canada
I enjoy reading and thinking about life. I have a flair for the dramatic. Woe betide the contributor who falls under my editorial pen. I am in several theatrical productions and I like to go camping in the Canadian wilds. My comment on brains: I wish I had one.
Darius
10 years old
Lafayette, CA, USA
I am in fifth grade. In my free time I enjoy reading and computer programming. As a hobby, I make useful objects and experiment with devices. I am very interested in the environment and was one of the founders of my school’s green committee. I enjoy reading about science, particularly chemistry, biology, and neuroscience.
Marin
8 years old
Cambridge, MA, USA
3rd grader who plays the piano and loves to sing and dance. She participates in Science Club for Girls and she and her Mom will be performing in their second opera this year.
Eleanor
8 years old
Champaign, IL, USA
I like reading and drawing. My favorite colors are blue, silver, pink, and purple. My favorite food is creamed spinach. I like to go shopping with my Mom.
….
At age 8, I would have been less Marin and more Eleanor. I hated opera; my father made us listen every Sunday afternoon during the winters.
Here’s something from an article about brain-machine interfaces for the final excerpt from the website (from the articles webpage),
![[downloaded from http://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/brain-machine_interfaces/7/]](http://www.frogheart.ca/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/brain-machineInterface-300x149.png)
[downloaded from http://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/brain-machine_interfaces/7/]
I think this piece written by Jose M. Carmena and José del R. Millán and reviewed by Bhargavi, 13 years old, is a good beginner’s piece for any adults who might be interested, as well as,, the journal’s target audience. This illustration the scientists have provided is very helpful to anyone who, for whatever reason, isn’t that knowledgeable about this area of research,
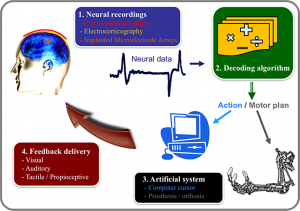
Figure 1 – Your brain in action:
the different components of a BMI include the recording system, the decoding algorithm, device to be controlled, and the feedback delivered to the user (modified from Heliot and Carmena, 2010).
As for getting information about basic details, here’s some of what I unearthed. The parent organization, ‘Frontiers in’ is based in Switzerland and describes itself this way on its About page,
Frontiers is a community-oriented open-access academic publisher and research network.
Our grand vision is to build an Open Science platform that empowers researchers in their daily work and where everybody has equal opportunity to seek, share and generate knowledge.
Frontiers is at the forefront of building the ultimate Open Science platform. We are driving innovations and new technologies around peer-review, article and author impact metrics, social networking for researchers, and a whole ecosystem of open science tools. We are the first – and only – platform that combines open-access publishing with research networking, with the goal to increase the reach of publications and ultimately the impact of articles and their authors.
Frontiers was launched as a grassroots initiative in 2007 by scientists from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne, Switzerland, out of the collective desire to improve the publishing options and provide better tools and services to researchers in the Internet age. Since then, Frontiers has become the fastest-growing open-access scholarly publisher, with a rapidly growing number of community-driven journals, more than 25,000 of high-impact researchers across a wide range of academic fields serving on the editorial boards and more than 4 million monthly page views.
As of a Feb. 27, 2013 news release, Frontiers has partnered with the Nature Publishing Group (NPG), Note: Links have been removed,
Emerging publisher Frontiers is joining Nature Publishing Group (NPG) in a strategic alliance to advance the global open science movement.
NPG, publisher of Nature, today announces a majority investment in the Swiss-based open access (OA) publisher Frontiers.
NPG and Frontiers will work together to empower researchers to change the way science is communicated, through open access publication and open science tools. Frontiers, led by CEO and neuroscientist Kamila Markram, will continue to operate with its own platform, brands, and policies.
Founded by scientists from École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in 2007, Frontiers is one of the fastest growing open access publishers, more than doubling articles published year on year. Frontiers now has a portfolio of open access journals in 14 fields of science and medicine, and published over 5,000 OA articles in 2012.
Working with NPG, the journal series “Frontiers in” will significantly expand in 2013-2014. Currently, sixty-three journals published by NPG offer open access options or are open access and NPG published over 2000 open access articles in 2012. Bilateral links between nature.com and frontiersin.org will ensure that open access papers are visible on both sites.
Frontiers and NPG will also be working together on innovations in open science tools, networking, and publication processes.
Frontiers is based at EPFL in Switzerland, and works out of Innovation Square, a technology park supporting science start-ups, and hosting R&D divisions of large companies such as Logitech & Nestlé.
As for this new venture, Frontiers for Young Minds, this appears to have been launched on Nov. 11, 2013. At least, that’s what I understand from this notice on Frontier’s Facebook page (Note: Links have been removed,
Frontiers
November 11 [2013?]
Great news for kids, parents, teachers and neuroscientists! We have just launched the first Frontiers for Young Minds!
Frontiers in #Neuroscience for Young Minds is an #openaccess scientific journal that involves young people in the review of articles.
This has the double benefit of bringing kids into the world of science and offering scientists a platform for reaching out to the broadest of all audiences.
Frontiers for Young Minds is science edited for kids, by kids. Learn more and spread the word! http://bit.ly/1dijipy #sfn13
I am glad to see this effort and I wish all the parties involved the best of luck.
![[downloaded from http://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/brain-machine_interfaces/7/]](http://www.frogheart.ca/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/brain-machineInterface-300x149.png)
