Following on my August 29, 2018 post (Sexbots, sexbot ethics, families, and marriage), I’m following up with a more general piece.
Robots, AI (artificial intelligence), and androids (humanoid robots), the terms can be confusing since there’s a tendency to use them interchangeably. Confession: I do it too, but, not this time. That said, I have multiple news bits.
Killer ‘bots and ethics
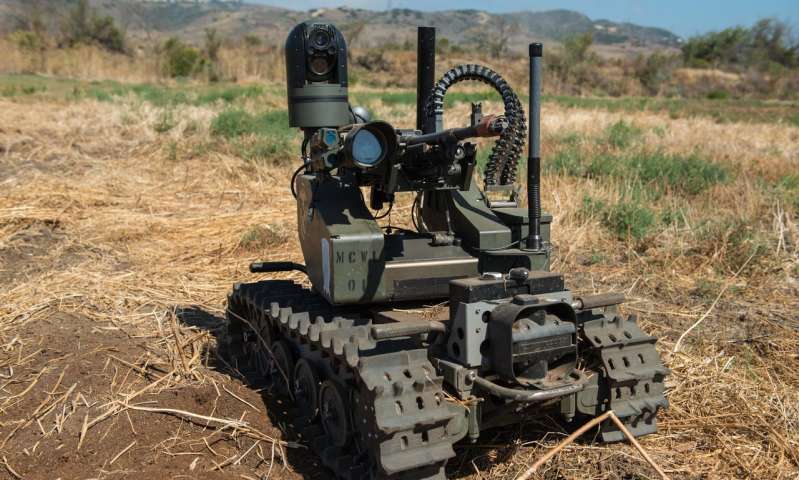

The U.S. military is already testing a Modular Advanced Armed Robotic System. Credit: Lance Cpl. Julien Rodarte, U.S. Marine Corps
That is a robot.
For the purposes of this posting, a robot is a piece of hardware which may or may not include an AI system and does not mimic a human or other biological organism such that you might, under circumstances, mistake the robot for a biological organism.
As for what precipitated this feature (in part), it seems there’s been a United Nations meeting in Geneva, Switzerland held from August 27 – 31, 2018 about war and the use of autonomous robots, i.e., robots equipped with AI systems and designed for independent action. BTW, it’s the not first meeting the UN has held on this topic.
Bonnie Docherty, lecturer on law and associate director of armed conflict and civilian protection, international human rights clinic, Harvard Law School, has written an August 21, 2018 essay on The Conversation (also on phys.org) describing the history and the current rules around the conduct of war, as well as, outlining the issues with the military use of autonomous robots (Note: Links have been removed),
When drafting a treaty on the laws of war at the end of the 19th century, diplomats could not foresee the future of weapons development. But they did adopt a legal and moral standard for judging new technology not covered by existing treaty language.
This standard, known as the Martens Clause, has survived generations of international humanitarian law and gained renewed relevance in a world where autonomous weapons are on the brink of making their own determinations about whom to shoot and when. The Martens Clause calls on countries not to use weapons that depart “from the principles of humanity and from the dictates of public conscience.”
I was the lead author of a new report by Human Rights Watch and the Harvard Law School International Human Rights Clinic that explains why fully autonomous weapons would run counter to the principles of humanity and the dictates of public conscience. We found that to comply with the Martens Clause, countries should adopt a treaty banning the development, production and use of these weapons.
Representatives of more than 70 nations will gather from August 27 to 31 [2018] at the United Nations in Geneva to debate how to address the problems with what they call lethal autonomous weapon systems. These countries, which are parties to the Convention on Conventional Weapons, have discussed the issue for five years. My co-authors and I believe it is time they took action and agreed to start negotiating a ban next year.
Docherty elaborates on her points (Note: A link has been removed),
The Martens Clause provides a baseline of protection for civilians and soldiers in the absence of specific treaty law. The clause also sets out a standard for evaluating new situations and technologies that were not previously envisioned.
Fully autonomous weapons, sometimes called “killer robots,” would select and engage targets without meaningful human control. They would be a dangerous step beyond current armed drones because there would be no human in the loop to determine when to fire and at what target. Although fully autonomous weapons do not yet exist, China, Israel, Russia, South Korea, the United Kingdom and the United States are all working to develop them. They argue that the technology would process information faster and keep soldiers off the battlefield.
The possibility that fully autonomous weapons could soon become a reality makes it imperative for those and other countries to apply the Martens Clause and assess whether the technology would offend basic humanity and the public conscience. Our analysis finds that fully autonomous weapons would fail the test on both counts.
…
I encourage you to read the essay in its entirety and for anyone who thinks the discussion about ethics and killer ‘bots is new or limited to military use, there’s my July 25, 2016 posting about police use of a robot in Dallas, Texas. (I imagine the discussion predates 2016 but that’s the earliest instance I have here.)
Teacher bots
Robots come in many forms and this one is on the humanoid end of the spectum,
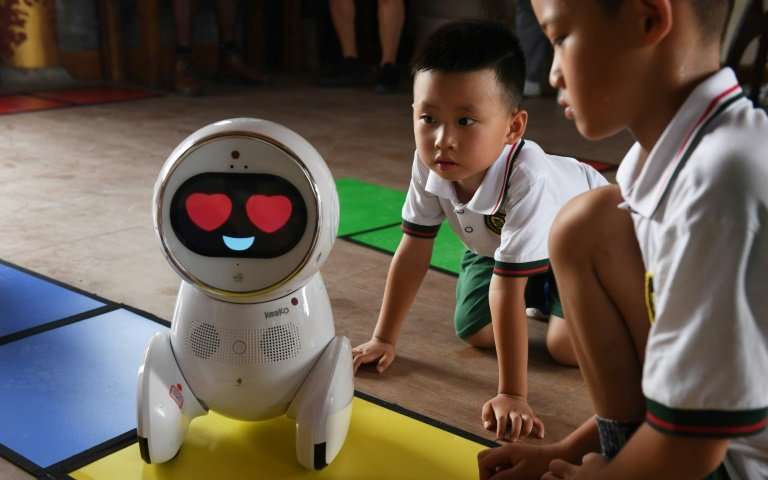

Children watch a Keeko robot at the Yiswind Institute of Multicultural Education in Beijing, where the intelligent machines are telling stories and challenging kids with logic problems [donwloaded from https://phys.org/news/2018-08-robot-teachers-invade-chinese-kindergartens.html]
Don’t those ‘eyes’ look almost heart-shaped? No wonder the kids love these robots, if an
August 29, 2018 news item on phys.org can be believed,
The Chinese kindergarten children giggled as they worked to solve puzzles assigned by their new teaching assistant: a roundish, short educator with a screen for a face.
Just under 60 centimetres (two feet) high, the autonomous robot named Keeko has been a hit in several kindergartens, telling stories and challenging children with logic problems.
Round and white with a tubby body, the armless robot zips around on tiny wheels, its inbuilt cameras doubling up both as navigational sensors and a front-facing camera allowing users to record video journals.
In China, robots are being developed to deliver groceries, provide companionship to the elderly, dispense legal advice and now, as Keeko’s creators hope, join the ranks of educators.
At the Yiswind Institute of Multicultural Education on the outskirts of Beijing, the children have been tasked to help a prince find his way through a desert—by putting together square mats that represent a path taken by the robot—part storytelling and part problem-solving.
Each time they get an answer right, the device reacts with delight, its face flashing heart-shaped eyes.
“Education today is no longer a one-way street, where the teacher teaches and students just learn,” said Candy Xiong, a teacher trained in early childhood education who now works with Keeko Robot Xiamen Technology as a trainer.
“When children see Keeko with its round head and body, it looks adorable and children love it. So when they see Keeko, they almost instantly take to it,” she added.
Keeko robots have entered more than 600 kindergartens across the country with its makers hoping to expand into Greater China and Southeast Asia.
Beijing has invested money and manpower in developing artificial intelligence as part of its “Made in China 2025” plan, with a Chinese firm last year unveiling the country’s first human-like robot that can hold simple conversations and make facial expressions.
According to the International Federation of Robots, China has the world’s top industrial robot stock, with some 340,000 units in factories across the country engaged in manufacturing and the automotive industry.
…
Moving on from hardware/software to a software only story.
AI fashion designer better than Balenciaga?
Despite the title for Katharine Schwab’s August 22, 2018 article for Fast Company, I don’t think this AI designer is better than Balenciaga but from the pictures I’ve seen the designs are as good and it does present some intriguing possibilities courtesy of its neural network (Note: Links have been removed),
The AI, created by researcher Robbie Barat, has created an entire collection based on Balenciaga’s previous styles. There’s a fabulous pink and red gradient jumpsuit that wraps all the way around the model’s feet–like a onesie for fashionistas–paired with a dark slouchy coat. There’s a textural color-blocked dress, paired with aqua-green tights. And for menswear, there’s a multi-colored, shimmery button-up with skinny jeans and mismatched shoes. None of these looks would be out of place on the runway.
To create the styles, Barat collected images of Balenciaga’s designs via the designer’s lookbooks, ad campaigns, runway shows, and online catalog over the last two months, and then used them to train the pix2pix neural net. While some of the images closely resemble humans wearing fashionable clothes, many others are a bit off–some models are missing distinct limbs, and don’t get me started on how creepy [emphasis mine] their faces are. Even if the outfits aren’t quite ready to be fabricated, Barat thinks that designers could potentially use a tool like this to find inspiration. Because it’s not constrained by human taste, style, and history, the AI comes up with designs that may never occur to a person. “I love how the network doesn’t really understand or care about symmetry,” Barat writes on Twitter.
You can see the ‘creepy’ faces and some of the designs here,
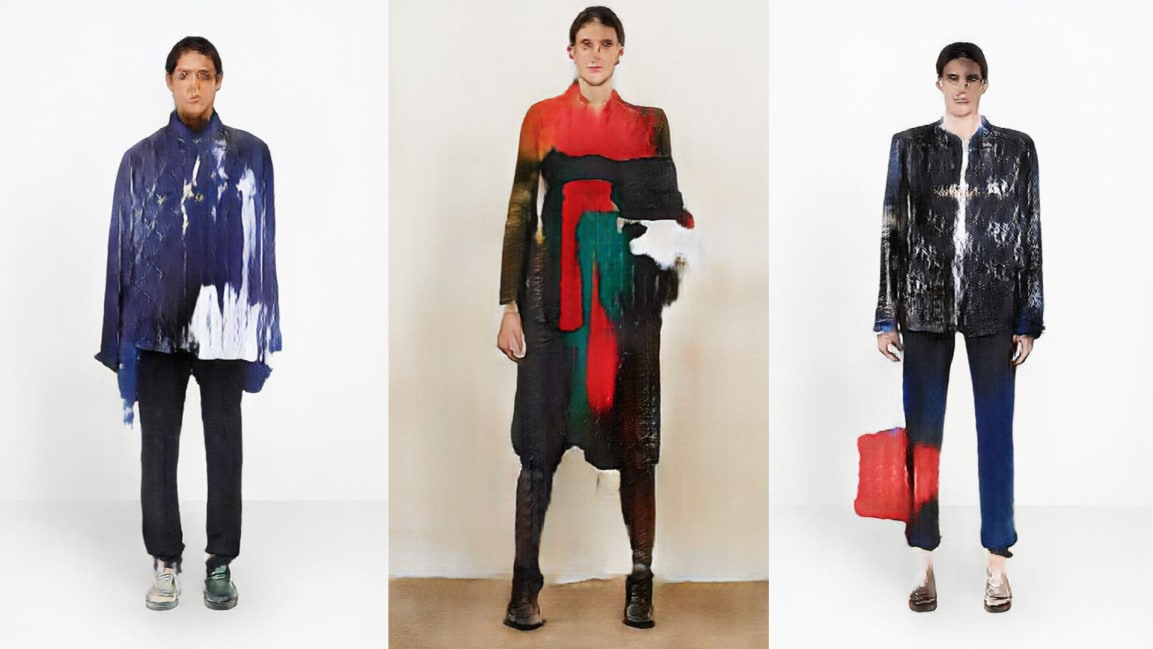

Image: Robbie Barat
In contrast to the previous two stories, this all about algorithms, no machinery with independent movement (robot hardware) needed.
Conversational android: Erica
Hiroshi Ishiguro and his lifelike (definitely humanoid) robots have featured here many, many times before. The most recent posting is a March 27, 2017 posting about his and his android’s participation at the 2017 SXSW festival.
His latest work is featured in an August 21, 2018 news news item on ScienceDaily,
We’ve all tried talking with devices, and in some cases they talk back. But, it’s a far cry from having a conversation with a real person.
Now a research team from Kyoto University, Osaka University, and the Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute, or ATR, have significantly upgraded the interaction system for conversational android ERICA, giving her even greater dialog skills.
ERICA is an android created by Hiroshi Ishiguro of Osaka University and ATR, specifically designed for natural conversation through incorporation of human-like facial expressions and gestures. The research team demonstrated the updates during a symposium at the National Museum of Emerging Science in Tokyo.
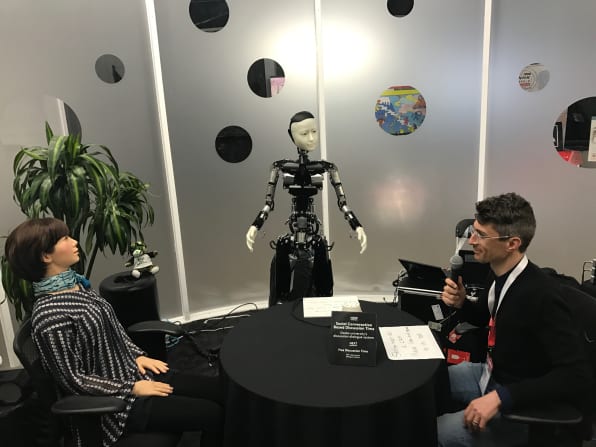
Here’s the latest conversational android, Erica
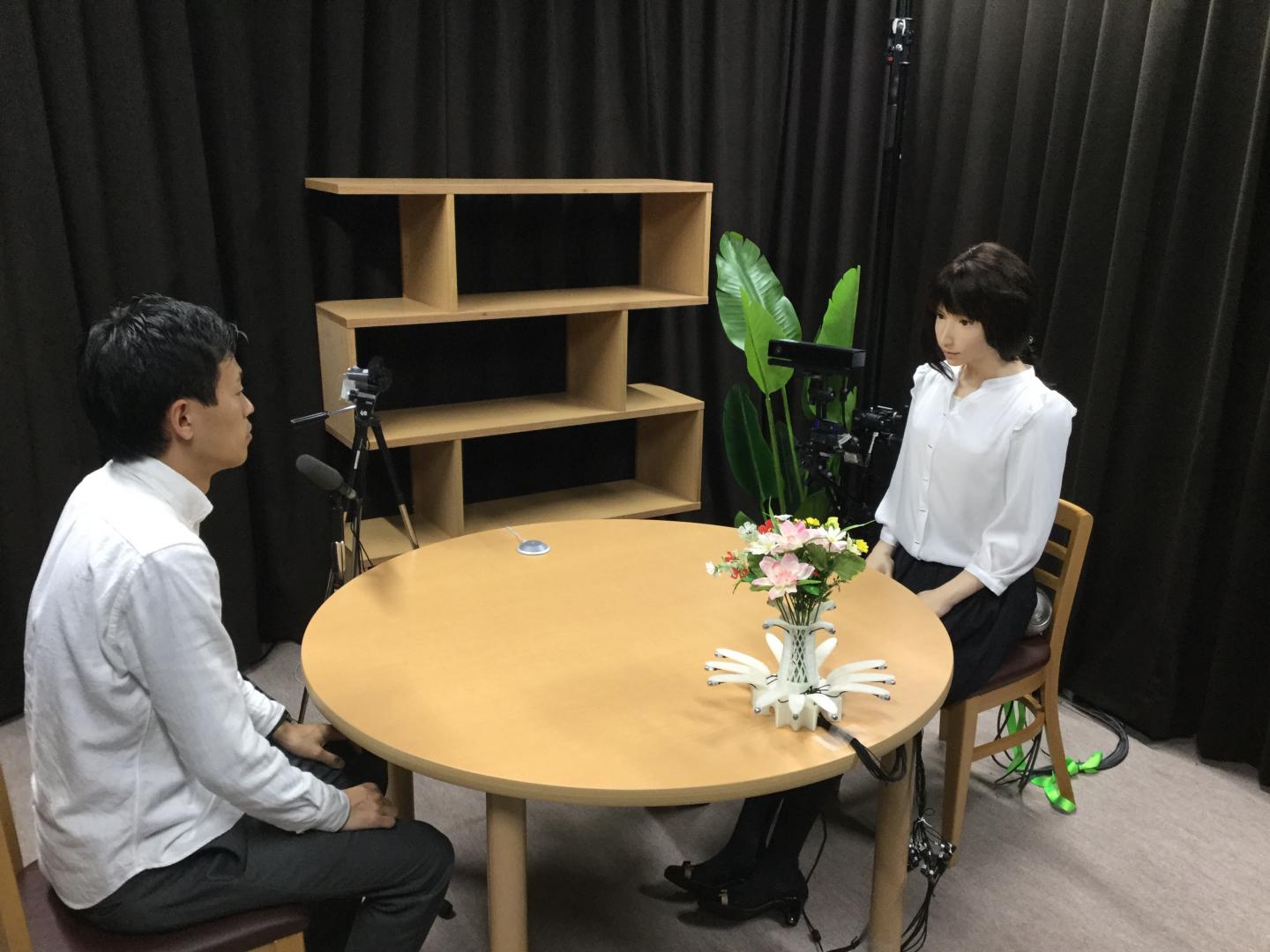

Caption: The experimental set up when the subject (left) talks with ERICA (right) Credit: Kyoto University / Kawahara lab
An August 20, 2018 Kyoto University press release on EurekAlert, which originated the news item, offers more details,
When we talk to one another, it’s never a simple back and forward progression of information,” states Tatsuya Kawahara of Kyoto University’s Graduate School of Informatics, and an expert in speech and audio processing.
“Listening is active. We express agreement by nodding or saying ‘uh-huh’ to maintain the momentum of conversation. This is called ‘backchanneling’, and is something we wanted to implement with ERICA.”
The team also focused on developing a system for ‘attentive listening’. This is when a listener asks elaborating questions, or repeats the last word of the speaker’s sentence, allowing for more engaging dialogue.
Deploying a series of distance sensors, facial recognition cameras, and microphone arrays, the team began collecting data on parameters necessary for a fluid dialog between ERICA and a human subject.
“We looked at three qualities when studying backchanneling,” continues Kawahara. “These were: timing — when a response happens; lexical form — what is being said; and prosody, or how the response happens.”
Responses were generated through machine learning using a counseling dialogue corpus, resulting in dramatically improved dialog engagement. Testing in five-minute sessions with a human subject, ERICA demonstrated significantly more dynamic speaking skill, including the use of backchanneling, partial repeats, and statement assessments.
“Making a human-like conversational robot is a major challenge,” states Kawahara. “This project reveals how much complexity there is in listening, which we might consider mundane. We are getting closer to a day where a robot can pass a Total Turing Test.”
Erica seems to have been first introduced publicly in Spring 2017, from an April 2017 Erica: Man Made webpage on The Guardian website,
Erica is 23. She has a beautiful, neutral face and speaks with a synthesised voice. She has a degree of autonomy – but can’t move her hands yet. Hiroshi Ishiguro is her ‘father’ and the bad boy of Japanese robotics. Together they will redefine what it means to be human and reveal that the future is closer than we might think.
Hiroshi Ishiguro and his colleague Dylan Glas are interested in what makes a human. Erica is their latest creation – a semi-autonomous android, the product of the most funded scientific project in Japan. But these men regard themselves as artists more than scientists, and the Erica project – the result of a collaboration between Osaka and Kyoto universities and the Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute International – is a philosophical one as much as technological one.
Erica is interviewed about her hope and dreams – to be able to leave her room and to be able to move her arms and legs. She likes to chat with visitors and has one of the most advanced speech synthesis systems yet developed. Can she be regarded as being alive or as a comparable being to ourselves? Will she help us to understand ourselves and our interactions as humans better?
Erica and her creators are interviewed in the science fiction atmosphere of Ishiguro’s laboratory, and this film asks how we might form close relationships with robots in the future. Ishiguro thinks that for Japanese people especially, everything has a soul, whether human or not. If we don’t understand how human hearts, minds and personalities work, can we truly claim that humans have authenticity that machines don’t?
Ishiguro and Glas want to release Erica and her fellow robots into human society. Soon, Erica may be an essential part of our everyday life, as one of the new children of humanity.
…
Key credits
- Director/Editor: Ilinca Calugareanu
- Producer: Mara Adina
- Executive producers for the Guardian: Charlie Phillips and Laurence Topham
- This video is produced in collaboration with the Sundance Institute Short Documentary Fund supported by the John D and Catherine T MacArthur Foundation
You can also view the 14 min. film here.
Artworks generated by an AI system are to be sold at Christie’s auction house
KC Ifeanyi’s August 22, 2018 article for Fast Company may send a chill down some artists’ spines,
For the first time in its 252-year history, Christie’s will auction artwork generated by artificial intelligence.
Created by the French art collective Obvious, “Portrait of Edmond de Belamy” is part of a series of paintings of the fictional Belamy family that was created using a two-part algorithm. …
…
The portrait is estimated to sell anywhere between $7,000-$10,000, and Obvious says the proceeds will go toward furthering its algorithm.
… Famed collector Nicolas Laugero-Lasserre bought one of Obvious’s Belamy works in February, which could’ve been written off as a novel purchase where the story behind it is worth more than the piece itself. However, with validation from a storied auction house like Christie’s, AI art could shake the contemporary art scene.
“Edmond de Belamy” goes up for auction from October 23-25 [2018].
Jobs safe from automation? Are there any?
Michael Grothaus expresses more optimism about future job markets than I’m feeling in an August 30, 2018 article for Fast Company,
…
A 2017 McKinsey Global Institute study of 800 occupations across 46 countries found that by 2030, 800 million people will lose their jobs to automation. That’s one-fifth of the global workforce. A further one-third of the global workforce will need to retrain if they want to keep their current jobs as well. And looking at the effects of automation on American jobs alone, researchers from Oxford University found that “47 percent of U.S. workers have a high probability of seeing their jobs automated over the next 20 years.”
The good news is that while the above stats are rightly cause for concern, they also reveal that 53% of American jobs and four-fifths of global jobs are unlikely to be affected by advances in artificial intelligence and robotics. But just what are those fields? I spoke to three experts in artificial intelligence, robotics, and human productivity to get their automation-proof career advice.
Creatives
“Although I believe every single job can, and will, benefit from a level of AI or robotic influence, there are some roles that, in my view, will never be replaced by technology,” says Tom Pickersgill, …
Maintenance foreman
When running a production line, problems and bottlenecks are inevitable–and usually that’s a bad thing. But in this case, those unavoidable issues will save human jobs because their solutions will require human ingenuity, says Mark Williams, head of product at People First, …
Hairdressers
Mat Hunter, director of the Central Research Laboratory, a tech-focused co-working space and accelerator for tech startups, have seen startups trying to create all kinds of new technologies, which has given him insight into just what machines can and can’t pull off. It’s lead him to believe that jobs like the humble hairdresser are safer from automation than those of, says, accountancy.
…
Therapists and social workers
Another automation-proof career is likely to be one involved in helping people heal the mind, says Pickersgill. “People visit therapists because there is a need for emotional support and guidance. This can only be provided through real human interaction–by someone who can empathize and understand, and who can offer advice based on shared experiences, rather than just data-driven logic.”
…
Teachers
Teachers are so often the unsung heroes of our society. They are overworked and underpaid–yet charged with one of the most important tasks anyone can have: nurturing the growth of young people. The good news for teachers is that their jobs won’t be going anywhere.
…
Healthcare workers
Doctors and nurses will also likely never see their jobs taken by automation, says Williams. While automation will no doubt better enhance the treatments provided by doctors and nurses the fact of the matter is that robots aren’t going to outdo healthcare workers’ ability to connect with patients and make them feel understood the way a human can.
…
Caretakers
While humans might be fine with robots flipping their burgers and artificial intelligence managing their finances, being comfortable with a robot nannying your children or looking after your elderly mother is a much bigger ask. And that’s to say nothing of the fact that even today’s most advanced robots don’t have the physical dexterity to perform the movements and actions carers do every day.
…
Grothaus does offer a proviso in his conclusion: certain types of jobs are relatively safe until developers learn to replicate qualities such as empathy in robots/AI.
It’s very confusing
There’s so much news about robots, artificial intelligence, androids, and cyborgs that it’s hard to keep up with it let alone attempt to get a feeling for where all this might be headed. When you add the fact that the term robots/artificial inteligence are often used interchangeably and that the distinction between robots/androids/cyborgs is not always clear any attempts to peer into the future become even more challenging.
At this point I content myself with tracking the situation and finding definitions so I can better understand what I’m tracking. Carmen Wong’s August 23, 2018 posting on the Signals blog published by Canada’s Centre for Commercialization of Regenerative Medicine (CCRM) offers some useful definitions in the context of an article about the use of artificial intelligence in the life sciences, particularly in Canada (Note: Links have been removed),
Artificial intelligence (AI). Machine learning. To most people, these are just buzzwords and synonymous. Whether or not we fully understand what both are, they are slowly integrating into our everyday lives. Virtual assistants such as Siri? AI is at work. The personalized ads you see when you are browsing on the web or movie recommendations provided on Netflix? Thank AI for that too.
AI is defined as machines having intelligence that imitates human behaviour such as learning, planning and problem solving. A process used to achieve AI is called machine learning, where a computer uses lots of data to “train” or “teach” itself, without human intervention, to accomplish a pre-determined task. Essentially, the computer keeps on modifying its algorithm based on the information provided to get to the desired goal.
Another term you may have heard of is deep learning. Deep learning is a particular type of machine learning where algorithms are set up like the structure and function of human brains. It is similar to a network of brain cells interconnecting with each other.
Toronto has seen its fair share of media-worthy AI activity. The Government of Canada, Government of Ontario, industry and multiple universities came together in March 2018 to launch the Vector Institute, with the goal of using AI to promote economic growth and improve the lives of Canadians. In May, Samsung opened its AI Centre in the MaRS Discovery District, joining a network of Samsung centres located in California, United Kingdom and Russia.
There has been a boom in AI companies over the past few years, which span a variety of industries. This year’s ranking of the top 100 most promising private AI companies covers 25 fields with cybersecurity, enterprise and robotics being the hot focus areas.
Wong goes on to explore AI deployment in the life sciences and concludes that human scientists and doctors will still be needed although she does note this in closing (Note: A link has been removed),
More importantly, empathy and support from a fellow human being could never be fully replaced by a machine (could it?), but maybe this will change in the future. We will just have to wait and see.
Artificial empathy is the term used in Lisa Morgan’s April 25, 2018 article for Information Week which unfortunately does not include any links to actual projects or researchers working on artificial empathy. Instead, the article is focused on how business interests and marketers would like to see it employed. FWIW, I have found a few references: (1) Artificial empathy Wikipedia essay (look for the references at the end of the essay for more) and (2) this open access article: Towards Artificial Empathy; How Can Artificial Empathy Follow the Developmental Pathway of Natural Empathy? by Minoru Asada.
Please let me know in the comments if you should have an insights on the matter in the comments section of this blog.








![In her series “What About the Heart?,” British photographer Luisa Whitton documents one of the creepiest niches of the Japanese robotics industry--androids. Here, an eerily lifelike face made for a robot. [dowloaded from http://www.fastcodesign.com/3031125/exposure/japans-uncanny-quest-to-humanize-robots?partner=rss]](http://www.frogheart.ca/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/What-About-the-Heart.jpg)