It looks like a popsicle to me,
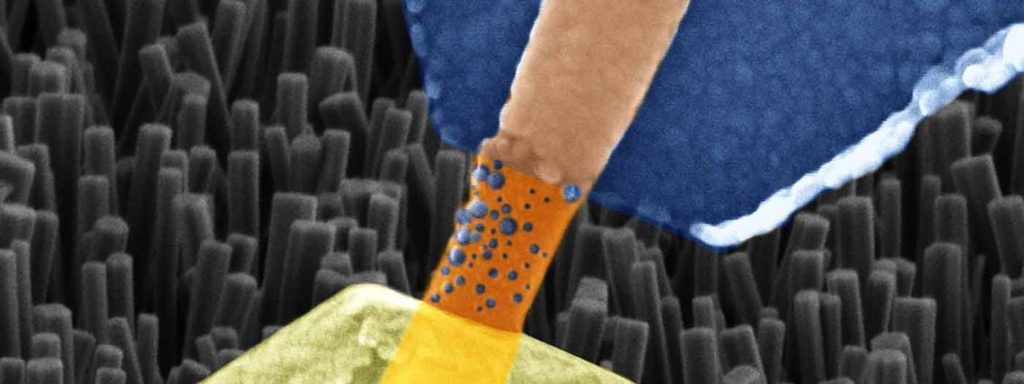
Caption: Image captured by an electron microscope of a single nanowire memristor (highlighted in colour to distinguish it from other nanowires in the background image). Blue: silver electrode, orange: nanowire, yellow: platinum electrode. Blue bubbles are dispersed over the nanowire. They are made up of silver ions and form a bridge between the electrodes which increases the resistance. Credit: Forschungszentrum Jülich
Not a popsicle but a representation of a device (memristor) scientists claim mimics a biological nerve cell according to a December 5, 2018 news item on ScienceDaily,
Scientists from Jülich [Germany] together with colleagues from Aachen [Germany] and Turin [Italy] have produced a memristive element made from nanowires that functions in much the same way as a biological nerve cell. The component is able to both save and process information, as well as receive numerous signals in parallel. The resistive switching cell made from oxide crystal nanowires is thus proving to be the ideal candidate for use in building bioinspired “neuromorphic” processors, able to take over the diverse functions of biological synapses and neurons.
A Dec. 5, 2018 Forschungszentrum Jülich press release (also on EurekAlert), which originated the news item, provides more details,
Computers have learned a lot in recent years. Thanks to rapid progress in artificial intelligence they are now able to drive cars, translate texts, defeat world champions at chess, and much more besides. In doing so, one of the greatest challenges lies in the attempt to artificially reproduce the signal processing in the human brain. In neural networks, data are stored and processed to a high degree in parallel. Traditional computers on the other hand rapidly work through tasks in succession and clearly distinguish between the storing and processing of information. As a rule, neural networks can only be simulated in a very cumbersome and inefficient way using conventional hardware.
Systems with neuromorphic chips that imitate the way the human brain works offer significant advantages. Experts in the field describe this type of bioinspired computer as being able to work in a decentralised way, having at its disposal a multitude of processors, which, like neurons in the brain, are connected to each other by networks. If a processor breaks down, another can take over its function. What is more, just like in the brain, where practice leads to improved signal transfer, a bioinspired processor should have the capacity to learn.
“With today’s semiconductor technology, these functions are to some extent already achievable. These systems are however suitable for particular applications and require a lot of space and energy,” says Dr. Ilia Valov from Forschungszentrum Jülich. “Our nanowire devices made from zinc oxide crystals can inherently process and even store information, as well as being extremely small and energy efficient,” explains the researcher from Jülich’s Peter Grünberg Institute.
For years memristive cells have been ascribed the best chances of being capable of taking over the function of neurons and synapses in bioinspired computers. They alter their electrical resistance depending on the intensity and direction of the electric current flowing through them. In contrast to conventional transistors, their last resistance value remains intact even when the electric current is switched off. Memristors are thus fundamentally capable of learning.
In order to create these properties, scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University used a single zinc oxide nanowire, produced by their colleagues from the polytechnic university in Turin. Measuring approximately one ten-thousandth of a millimeter in size, this type of nanowire is over a thousand times thinner than a human hair. The resulting memristive component not only takes up a tiny amount of space, but also is able to switch much faster than flash memory.
Nanowires offer promising novel physical properties compared to other solids and are used among other things in the development of new types of solar cells, sensors, batteries and computer chips. Their manufacture is comparatively simple. Nanowires result from the evaporation deposition of specified materials onto a suitable substrate, where they practically grow of their own accord.
In order to create a functioning cell, both ends of the nanowire must be attached to suitable metals, in this case platinum and silver. The metals function as electrodes, and in addition, release ions triggered by an appropriate electric current. The metal ions are able to spread over the surface of the wire and build a bridge to alter its conductivity.
Components made from single nanowires are, however, still too isolated to be of practical use in chips. Consequently, the next step being planned by the Jülich and Turin researchers is to produce and study a memristive element, composed of a larger, relatively easy to generate group of several hundred nanowires offering more exciting functionalities.
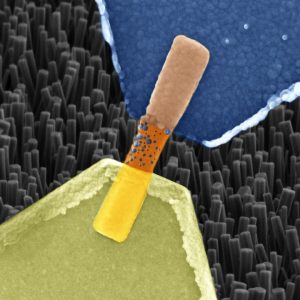
The Italians have also written about the work in a December 4, 2018 news item for the Polytecnico di Torino’s inhouse magazine, PoliFlash’. I like the image they’ve used better as it offers a bit more detail and looks less like a popsicle. First, the image,
Now, the news item, which includes some historical information about the memristor (Note: There is some repetition and links have been removed),
Emulating and understanding the human brain is one of the most important challenges for modern technology: on the one hand, the ability to artificially reproduce the processing of brain signals is one of the cornerstones for the development of artificial intelligence, while on the other the understanding of the cognitive processes at the base of the human mind is still far away.
And the research published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications by Gianluca Milano and Carlo Ricciardi, PhD student and professor, respectively, of the Applied Science and Technology Department of the Politecnico di Torino, represents a step forward in these directions. In fact, the study entitled “Self-limited single nanowire systems combining all-in-one memristive and neuromorphic functionalities” shows how it is possible to artificially emulate the activity of synapses, i.e. the connections between neurons that regulate the learning processes in our brain, in a single “nanowire” with a diameter thousands of times smaller than that of a hair.
It is a crystalline nanowire that takes the “memristor”, the electronic device able to artificially reproduce the functions of biological synapses, to a more performing level. Thanks to the use of nanotechnologies, which allow the manipulation of matter at the atomic level, it was for the first time possible to combine into one single device the synaptic functions that were individually emulated through specific devices. For this reason, the nanowire allows an extreme miniaturisation of the “memristor”, significantly reducing the complexity and energy consumption of the electronic circuits necessary for the implementation of learning algorithms.
Starting from the theorisation of the “memristor” in 1971 by Prof. Leon Chua – now visiting professor at the Politecnico di Torino, who was conferred an honorary degree by the University in 2015 – this new technology will not only allow smaller and more performing devices to be created for the implementation of increasingly “intelligent” computers, but is also a significant step forward for the emulation and understanding of the functioning of the brain.
“The nanowire memristor – said Carlo Ricciardi – represents a model system for the study of physical and electrochemical phenomena that govern biological synapses at the nanoscale. The work is the result of the collaboration between our research team and the RWTH University of Aachen in Germany, supported by INRiM, the National Institute of Metrological Research, and IIT, the Italian Institute of Technology.”
h.t for the Italian info. to Nanowerk’s Dec. 10, 2018 news item.
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Self-limited single nanowire systems combining all-in-one memristive and neuromorphic functionalities by Gianluca Milano, Michael Luebben, Zheng Ma, Rafal Dunin-Borkowski, Luca Boarino, Candido F. Pirri, Rainer Waser, Carlo Ricciardi, & Ilia Valov. Nature Communicationsvolume 9, Article number: 5151 (2018) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07330-7 Published: 04 December 2018
This paper is open access.
Just use the search term “memristor” in the blog search engine if you’re curious about the multitudinous number of postings on the topic here.