Protein folding doesn’t seem all that exciting to me and the notion that it might lead to self-assembled, living machines isn’t all that new (see my May 31, 2012 posting about a Living Foundries project). So the June 10, 2012 news item on Nanowerk left me with a flat feeling, initially,
Enabling bioengineers to design new molecular machines for nanotechnology applications is one of the possible outcomes of a study by University of Montreal researchers that was published in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology today (“Visualizing transient protein folding intermediates by tryptophan scanning mutagenesis” [behind a paywall]). The scientists have developed a new approach to visualize how proteins assemble, which may also significantly aid our understanding of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, which are caused by errors in assembly.
“In order to survive, all creatures, from bacteria to humans, monitor and transform their environments using small protein nanomachines made of thousands of atoms,” explained the senior author of the study, Prof. Stephen Michnick of the university’s department of biochemistry. “For example, in our sinuses, there are complex receptor proteins that are activated in the presence of different odor molecules. Some of those scents warn us of danger; others tell us that food is nearby.” Proteins are made of long linear chains of amino acids, which have evolved over millions of years to self-assemble extremely rapidly – often within thousandths of a split second – into a working nanomachine.
My ears pricked up when the talk turned to capturing images of action, which occurs in a “fleetingly short time,”
“To understand how a protein goes from a linear chain to a unique assembled structure, we need to capture snapshots of its shape at each stage of assembly said Dr. Alexis Vallée-Bélisle, first author of the study. “The problem is that each step exists for a fleetingly short time and no available technique enables us to obtain precise structural information on these states within such a small time frame. We developed a strategy to monitor protein assembly by integrating fluorescent probes throughout the linear protein chain so that we could detect the structure of each stage of protein assembly, step by step to its final structure.” The protein assembly process is not the end of its journey, as a protein can change, through chemical modifications or with age, to take on different forms and functions. “Understanding how a protein goes from being one thing to becoming another is the first step towards understanding and designing protein nanomachines for biotechnologies such as medical and environmental diagnostic sensors, drug synthesis or delivery,” Vallée-Bélisle said.
Here’s an image of protein self-assembly from the University of Montreal (Université de Montréal) website (Montréal, Québec, Canada),
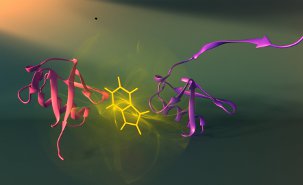
Vallée-Bélisle and Michnick have developed a new approach to visualize how proteins assemble, which may also significantly aid our understanding of diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, which are caused by errors in assembly. Here shown are two different assembly stages (purple and red) of the protein ubiquitin and the fluorescent probe used to visualize these stage (tryptophan: see yellow). Credit: Peter Allen
I would have liked a little more detail (e.g. how little time is there to capture the images?) but there isn’t always time either for the people who write these news releases or for me to follow up with questions. Given the huge political unrest amongst students over the proposed tuition fees and the Québec government’s attempts (sometimes described as draconian) to impose order, I’m impressed this news release was pulled together.