The peculiar property of turning ice-like at room temperatures occurs with water at the nanscale according to an Aug. 29, 2016 news item on phys.org,
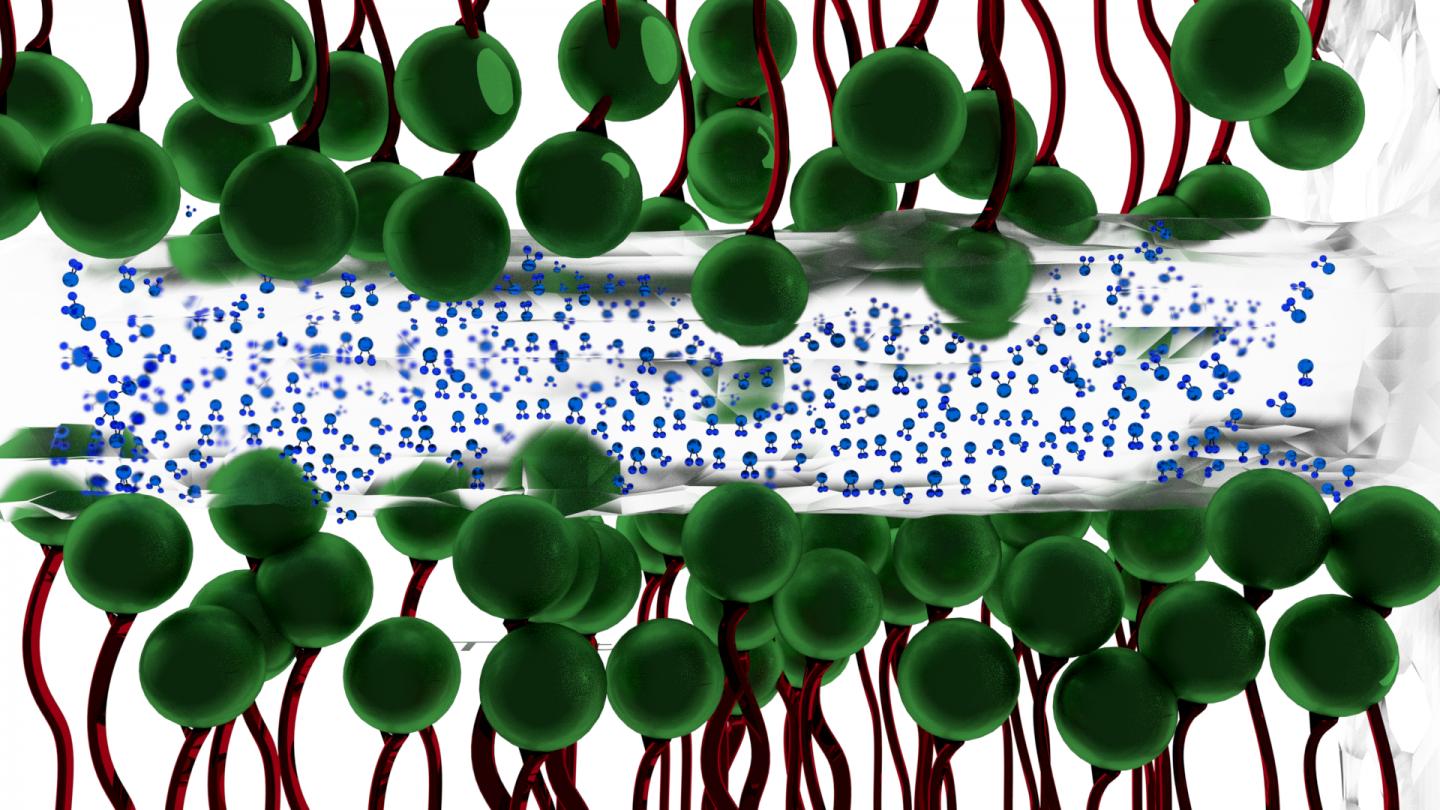
New research by scientists at The University of Akron (UA) [Ohio, US] shows that a nanometer-thin layer of water between two charged surfaces exhibits ice-like tendencies that allow it to withstand pressures of hundreds of atmospheres. The discovery could lead to better ways to minimize friction in a variety of settings.
An Aug. 29, 2016 University of Akron news release on EurekAlert, which originated the news item, elaborates on the theme,
Why water between two surfaces does not always simply squeeze out when placed under severe pressure had never been fully understood. The UA researchers discovered that naturally-occurring charges between two surfaces under intense pressure traps the water, and gives it ice-like qualities. It is this ice-like layer of water–occurring at room temperature–that then lessens the friction between the two surfaces.
“For the first time we have a basic understanding of what happens to water under these conditions and why it keeps two surfaces apart,” says Professor Ali Dhinojwala. “We had suspected something was happening at the molecular level, and now we have proof.”
“This discovery could lead to improved designs where low friction surfaces are critically important, such as in biomedical knee implants,” says UA graduate student Nishad Dhopatkar.
Graduate student Adrian Defante, who was also part of the research team, says “the newfound properties of water might contribute to the development of more effective antimicrobial coatings, as a thin layer of water could prevent bacterial adhesion.”
Dhinojwala adds that the research conversely offers insight into how water might be kept away from two surfaces, which could lead to better adhesives in watery environments.
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Ice-like water supports hydration forces and eases sliding friction by Nishad Dhopatkar, Adrian P. Defante, and Ali Dhinojwala. Science Advances 26 Aug 2016: Vol. 2, no. 8, e1600763 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1600763 Published 03 August 2016
This paper is open access.
Here’s an image the researchers are using to illustrate their work