A School of Dentistry, at the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) or elsewhere, is not my first thought as a likely source for work on improving glaucoma treatment—it turns out that I’m a bit shortsighted (pun intended). A Feb. 14, 2014 news item on Azonano describes the issue with glaucoma treatment and a new delivery system for it developed by a research team at UCLA,
By 2020, nearly 80 million people are expected to have glaucoma, a disorder of the eye that, if left untreated, can damage the optic nerve and eventually lead to blindness.
The disease often causes pressure in the eye due to a buildup of fluid and a breakdown of the tissue that is responsible for regulating fluid drainage. Doctors commonly treat glaucoma using eye drops that can help the eye drain or decrease fluid production.
Unfortunately, patients frequently have a hard time sticking to the dosing schedules prescribed by their doctors, and the medication — when administered through drops — can cause side effects in the eye and other parts of the body.
In what could be a significant step toward improving the management of glaucoma, researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry have created a drug delivery system that may have less severe side effects than traditional glaucoma medication and improve patients’ ability to comply with their prescribed treatments. The scientists bound together glaucoma-fighting drugs with nanodiamonds and embedded them onto contact lenses. The drugs are released into the eye when they interact with the patient’s tears.
The new technology showed great promise for sustained glaucoma treatment and, as a side benefit, the nanodiamond-drug compound even improved the contact lenses’ durability.
The Feb. 13, 2014 UCLA news release by Brianna Deane, which originated the news item, describes the nanodiamonds and how they were employed in this project,
Nanodiamonds, which are byproducts of conventional mining and refining processes, are approximately five nanometers in diameter and are shaped like tiny soccer balls. They can be used to bind a wide spectrum of drug compounds and enable drugs to be released into the body over a long period of time.
To deliver a steady release of medication into the eye, the UCLA researchers combined nanodiamonds with timolol maleate, which is commonly used in eye drops to manage glaucoma. When applied to the nanodiamond-embedded lenses, timolol is released when it comes into contact with lysozyme, an enzyme that is abundant in tears.
“Delivering timolol through exposure to tears may prevent premature drug release when the contact lenses are in storage and may serve as a smarter route toward drug delivery from a contact lens.” said Kangyi Zhang, co-first author of the study and a graduate student in Ho’s lab.
One of the drawbacks of traditional timolol maleate drops is that as little as 5 percent of the drug actually reaches the intended site. Another disadvantage is burst release, where a majority of the drug is delivered too quickly, which can cause significant amounts of the drug to “leak” or spill out of the eye and, in the most serious cases, can cause complications such as an irregular heartbeat. Drops also can be uncomfortable to administer, which leads many patients to stop using their medication.
But the contact lenses developed by the UCLA team successfully avoided the burst release effect. The activity of the released timolol was verified by a primary human-cell study.
“In addition to nanodiamonds’ promise as triggered drug-delivery agents for eye diseases, they can also make the contact lenses more durable during the course of insertion, use and removal, and more comfortable to wear,” said Ho, who is also a professor of bioengineering and a member of the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center and the California NanoSystems Institute.
Even with the nanodiamonds embedded, the lenses still possessed favorable levels of optical clarity. And, although mechanical testing verified that they were stronger than normal lenses, there were no apparent changes to water content, meaning that the contact lenses’ comfort and permeability to oxygen would likely be preserved.
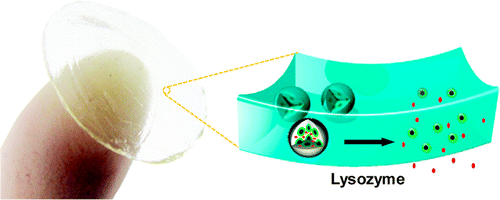
By this time, I was madly curious as to what these contact lenses might look like and so I found this image, accompanying the researchers’ paper, showing what looks like a standard contact lens with an illustration of how the artist imagines the diamonds and medications are functioning at the nanoscale,
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,Diamond Nanogel-Embedded Contact Lenses Mediate Lysozyme-Dependent Therapeutic Release by Ho-Joong Kim, Kangyi Zhang, Laura Moore, and Dean Ho. ACS Nano, Article ASAP DOI: 10.1021/nn5002968 Publication Date (Web): February 8, 2014
Copyright © 2014 American Chemical Society
This paper is behind a paywall.