Setting the stage
Not unexpectedly, CRISPR-Cas9 or clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-CRISPR-associated protein 9 can be dangerous as these scientists note in a July 16, 2018 news item on phys.org,
Scientists at the Wellcome Sanger Institute have discovered that CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing can cause greater genetic damage in cells than was previously thought. These results create safety implications for gene therapies using CRISPR/Cas9 in the future as the unexpected damage could lead to dangerous changes in some cells.
Reported today (16 July 2018) in the journal Nature Biotechnology, the study also revealed that standard tests for detecting DNA changes miss finding this genetic damage, and that caution and specific testing will be required for any potential gene therapies.
This CRISPR-Cas9 image reminds me of popcorn,
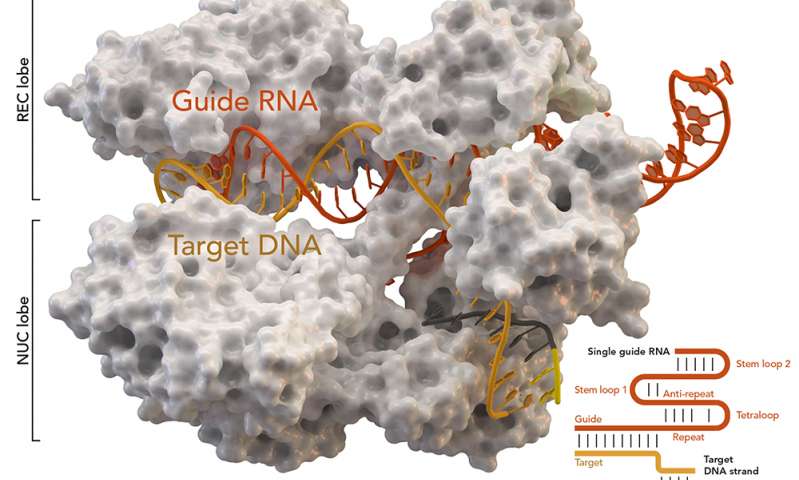
CRISPR-associated protein Cas9 (white) from Staphylococcus aureus based on Protein Database ID 5AXW. Credit: Thomas Splettstoesser (Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 4.0)[ downloaded from https://phys.org/news/2018-07-genome-crisprcas9-gene-higher-thought.html#jCp]
CRISPR/Cas9 is one of the newest genome editing tools. It can alter sections of DNA in cells by cutting at specific points and introducing changes at that location. Already extensively used in scientific research, CRISPR/Cas9 has also been seen as a promising way to create potential genome editing treatments for diseases such as HIV, cancer or sickle cell disease. Such therapeutics could inactivate a disease-causing gene, or correct a genetic mutation. However, any potential treatments would have to prove that they were safe.
Previous research had not shown many unforeseen mutations from CRISPR/Cas9 in the DNA at the genome editing target site. To investigate this further the researchers carried out a full systematic study in both mouse and human cells and discovered that CRISPR/Cas9 frequently caused extensive mutations, but at a greater distance from the target site.
The researchers found many of the cells had large genetic rearrangements such as DNA deletions and insertions. These could lead to important genes being switched on or off, which could have major implications for CRISPR/Cas9 use in therapies. In addition, some of these changes were too far away from the target site to be seen with standard genotyping methods.
Prof Allan Bradley, corresponding author on the study from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “This is the first systematic assessment of unexpected events resulting from CRISPR/Cas9 editing in therapeutically relevant cells, and we found that changes in the DNA have been seriously underestimated before now. It is important that anyone thinking of using this technology for gene therapy proceeds with caution, and looks very carefully to check for possible harmful effects.”
Michael Kosicki, the first author from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “My initial experiment used CRISPR/Cas9 as a tool to study gene activity, however it became clear that something unexpected was happening. Once we realised the extent of the genetic rearrangements we studied it systematically, looking at different genes and different therapeutically relevant cell lines, and showed that the CRISPR/Cas9 effects held true.”
The work has implications for how CRISPR/Cas9 is used therapeutically and is likely to re-spark researchers’ interest in finding alternatives to the standard CRISPR/Cas9 method for gene editing.
Prof Maria Jasin, an independent researcher from Memorial Slone Kettering Cancer Centre, New York, who was not involved in the study said: “This study is the first to assess the repertoire of genomic damage arising at a CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage site. While it is not known if genomic sites in other cell lines will be affected in the same way, this study shows that further research and specific testing is needed before CRISPR/Cas9 is used clinically.”
For anyone who’d like to better understand the terms gene editing and CRISPR-Cas9, the Wellcome Sanger Institute provides these explanatory webpages, What is genome editing? and What is CRISPR-Cas9?
For the more advanced, here’s a link and a citation for the paper,
Repair of double-strand breaks induced by CRISPR–Cas9 leads to large deletions and complex rearrangements by Michael Kosicki, Kärt Tomberg, & Allan Bradley. Nature Biotechnology DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4192 Published 16 July 2018
This paper appears to be open access.
The kerfuffle
It seems this news has affected the CRISPR market. From a July 16, 2018 article by Cale Guthrie Weissman for Fast Company,
… CRISPR could unknowingly delete or alter non-targeted genes, which could lead to myriad unintended consequences. This is especially frightening, since the technology is going to be used in human clinical trials.
Meanwhile, other scientists working with CRISPR are trying to downplay the findings, telling STAT [a life sciences and business journalism website] that there have been no reported adverse effects similar to what the study describes. The news, however, has brought about a market reaction–at least three publicly traded companies that focus on CRISPR-based therapies are in stock nosedive. Crispr Therapeutics is down by over 6%; Editas fell by over 3%; and Intellia Therapeutics dropped by over 5%. [emphasis mine]
Damage control
Gaetan Burgio (geneticist, Australian National University) in a July 16, 2018 essay on phys.org (originating from The Conversation) suggests some calm (Note: Links have been removed),
…
But a new study has called into question the precision of the technique [CRISPR gene editing technology].
The hope for gene editing is that it will be able to cure and correct diseases. To date, many successes have been reported, including curing deafness in mice, and in altering cells to cure cancer.
Some 17 clinical trials in human patients are registered [emphasis mine] testing gene editing on leukaemias, brain cancers and sickle cell anaemia (where red blood cells are misshaped, causing them to die). Before implementing CRISPR technology in clinics to treat cancer or congenital disorders, we must address whether the technique is safe and accurate.
…
There are a few options for getting around this problem. One option is to isolate the cells we wish to edit from the body and reinject only the ones we know have been correctly edited.
For example, lymphocytes (white blood cells) that are crucial to killing cancer cells could be taken out of the body, then modified using CRISPR to heighten their cancer-killing properties. The DNA of these cells could be sequenced in detail, and only the cells accurately and specifically gene-modified would be selected and delivered back into the body to kill the cancer cells.
While this strategy is valid for cells we can isolate from the body, some cells, such as neurons and muscles, cannot be removed from the body. These types of cells might not be suitable for gene editing using Cas9 scissors.
Fortunately, researchers have discovered other forms of CRISPR systems that don’t require the DNA to be cut. Some CRISPR systems only cut the RNA, not the DNA (DNA contains genetic instructions, RNA convey the instructions on how to synthesise proteins).
As RNA [ribonucleic acid] remains in our cells only for a specific period of time before being degraded, this would allow us to control the timing and duration of the CRISPR system delivery and reverse it (so the scissors are only functional for a short period of time).
This was found to be successful for dementia in mice. Similarly, some CRISPR systems simply change the letters of the DNA, rather than cutting them. This was successful for specific mutations causing diseases such as hereditary deafness in mice.
I agree with Burgio’s conclusion (not included here) that we have a lot more to learn and I can’t help wondering why there are 17 registered human clinical trials at this point.