This research suggests that graphene flakes might have an impact on anxiety-related behaviour. If I read the work correctly, the graphene flakes don’t exacerbate anxiety but, instead, may provide relief.
A March 10, 2021 news item on phys.org announces the research into graphene flakes and neurons (rat), Note: Links have been removed,
Effective, specific, with a reversible and non-harmful action: the identikit of the perfect biomaterial seems to correspond to graphene flakes, the subject of a new study carried out by SISSA—International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste, Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2) of Barcelona, and the National Graphene Institute of the University of Manchester, as part of the European Graphene Flagship project. This nanomaterial has demonstrated the ability to interact with the functions of the nervous system in vertebrates in a very specific manner, interrupting the building up of a pathological process that leads to anxiety-related behavior.
“We previously showed that when graphene flakes are delivered to neurons they interfere spontaneously with excitatory synapses by transiently preventing glutamate release from presynaptic terminals,” says Laura Ballerini of SISSA, the leader of the team that carried out the research study “Graphene oxide prevents lateral amygdala dysfunctional synaptic plasticity and reverts long lasting anxiety behavior in rats,” recently published in Biomaterials.
…
A March 10, 2021 Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati (SISSA) press release (also on EurekAlert), which originated the news item, provides more detail,
“We investigated whether such a reduction in synaptic activity was sufficient to modify related behaviours, in particular the pathological ones that develop due to a transient and localised hyper-function of excitatory synapses”. This approach would fortify the strategy of selective and transient targeting of synapses to prevent the development of brain pathologies by using the so-called precise medicine treatments.
To test this hypothesis, the team focused on post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and carried out the experiments in two phases, in vivo and in vitro.
“We analysed defensive behaviours caused in rats [emphasis mine] by the presence of a predator, using the exposure to cat odour, to induce an aversive memory” explains Audrey Franceschi Biagioni of SISSA, the first author of the study. “If exposed to the predator odour, the rat has a defensive response, holing up, and this experience is so well-imprinted in the memory, that when the animal is placed in the same context even six days later, the animal remembers the odour of the predator and acts the same protective behaviour. This is a well-known and consolidated model, that we used to reproduce a stress behaviour. Exposure to the predator can modify neuronal connections – a phenomenon that is technically known as plasticity – and increases synaptic activity in a specific area of the amygdala that therefore represented the target of our study to test the effects of the nanomaterial”.
Laura Ballerini adds: “We hypothesised that graphene flakes that we showed to temporarily inhibit excitatory synapses (without causing inflammation, damage to neurons or other side effects) could be injected in the lateral amygdala when the plasticity associated with memory was consolidated. If the nanomaterial was efficient in blocking excitatory synapses, it should inhibit plasticity and decrease the anxiety related response. And this is what happened: the animals that were administered with graphene flakes, after six days, “forgot” the anxiety related responses, rescuing their behaviour”.
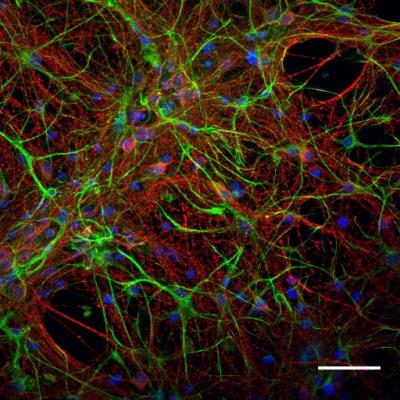
The second part of the research was performed in vitro. “In vivo we could observe only behavioural changes and could not evaluate the impact of the graphene flakes on synapses,” explains Giada Cellot, researcher at SISSA and first author of the study together with Audrey Franceschi Biagioni. “In vitro experiments allowed to work on a simplified model, to get insight about the mechanisms through which the graphene flakes can interact with neurons. We used neuronal cultures obtained from the amygdala, the region of the brain where the stress response occurs, and we observed that the effects of nanomaterials were specific for the excitatory synapses and a short exposure to graphene flakes could prevent the pathological plasticity of the synapses”.
Thanks to these findings, graphene flakes have shown their potential as nanotools (biomedical tools composed of nanomaterials) that could act in a specific and reversible way on synaptic activity to interrupt a pathological process and therefore they might be used also to transport drugs or for other applications in the field of precision medicine.
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Graphene oxide prevents lateral amygdala dysfunctional synaptic plasticity and reverts long lasting anxiety behavior in rats by Audrey Franceschi Biagionia1, Giada Cellot, Elisa Pati, Neus Lozano, Belén Ballesteros, Raffaele Casani, Norberto Cysne Coimbra, Kostas Kostarelos, Laura Ballerini. Biomaterials Volume 271, April 2021, 120749 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120749
This paper is open access.