it took a while to get there but the February 13, 2023 news item on phys.org announced research into extending memristors from tunable conductance to reconfigurable photo-response,
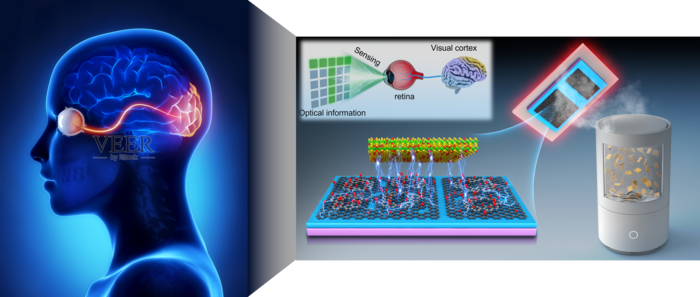
In traditional vision systems, the optical information is captured by a frame-based digital camera, and then the digital signal is processed afterwards using machine-learning algorithms. In this scenario, a large amount of data (mostly redundant) has to be transferred from a standalone sensing elements to the processing units, which leads to high latency and power consumption.
To address this problem, much effort has been devoted to developing an efficient approach, where some of the memory and computational tasks are offloaded to sensor elements that can perceive and process the optical signal simultaneously.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Weida Hu from School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China, State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China, and co-workers have developed a non-volatile photo-memristor, in which the reconfigurable responsivity can be modulated by the charge and/or photon flux through it and further stored in the device.
…
A February 13, 2023 Chinese Academy of Sciences press release, which originated the news item, provided more technical detail about the work,
The non-volatile photo-memristor has a simple two-terminal architecture, in which photoexcited carriers and oxygen-related ions are coupled, leading to a displaced and pinched hysteresis in the current-voltage characteristics. For the first time, non-volatile photo-memristors implement computationally complete logic with photoresponse-stateful operations, for which the same photo-memristor serves as both a logic gate and memory, using photoresponse as a physical state variable instead of light, voltage and memresistance. Polarity reversal of photo-memristors shows great potential for in-memory sensing and computing with feature extraction and image recognition for neuromorphic vision.
The photo-memristor demonstrates tunable short-circuit current in a non-volatile mode under illumination. By mimicking the biological functionalities of the human retina and designing specific device structures, the devices can act as neural network for neuromorphic visual processing and implementation of completely photoresponse-stateful logic operations triggered by electrical and light stimuli together. It can support various kinds of sensing tasks with all-in-one sensing-memory-computing approaches. These scientists summarize the operational principle and feature of their device:
“We design[ed] a two-terminal device with MoS2-xOx and specific graphene for three purposes in one: (1) to provide low barrier energy for the migration of oxygen ions; (2) to perform as geometry-asymmetric metal–semiconductor–metal van der Waals heterostructures with multi-photoresponse states; and (3) as an extension of a memristor, this device not only provides tunable conductance, but also demonstrates reconfigurable photoresponse for reading at zero bias voltage.”
“Moreover, the tunable short-circuit photocurrent and photoresponse can be increased to 889.8 nA and 98.8 mA/W, respectively, which are much higher than that of other reconfigurable phototransistors based on 2D materials. To reverse the channel polarity and obtain a gate-tunable short-circuit photocurrent, the channel semiconductor must be thin enough. Thus, it is difficult to use the thick film needed to absorb enough light to get a large signal. In our case, the mechanism of the two-terminal device rearrangement is based on ion migration, which is not limited by the thickness. We can increase the thickness of the film to absorb more photons and get a large short-circuit photocurrent.” they added.
“This new concept of a two-terminal photo-memristor not only enables all-in-one sensing-memory-computing approaches for neuromorphic vision hardware, but also brings great convenience for high-density integration.” the scientists forecast.
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Graphene/MoS2−xOx/graphene photomemristor with tunable non-volatile responsivities for neuromorphic vision processing by Xiao Fu, Tangxin Li, Bin Caid, Jinshui Miao, Gennady N. Panin, Xinyu Ma, Jinjin Wang, Xiaoyong Jiang, Qing Lia, Yi Dong, Chunhui Hao, Juyi Sun, Hangyu Xu, Qixiao Zhao, Mengjia Xia, Bo Song, Fansheng Chen, Xiaoshuang Chen, Wei Lu, Weida Hu. Light: Science & Applications volume 12, Article number: 39 (2023) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01079-5 Published: 07 February 2023
This paper is open access.