Does everything have to be ‘brainy’? Read on for the latest on ‘brainy’ devices.
An August 4, 2022 University of Chicago news release (also on EurekAlert) describes work on a stretchable neuromorphic chip, Note: Links have been removed,
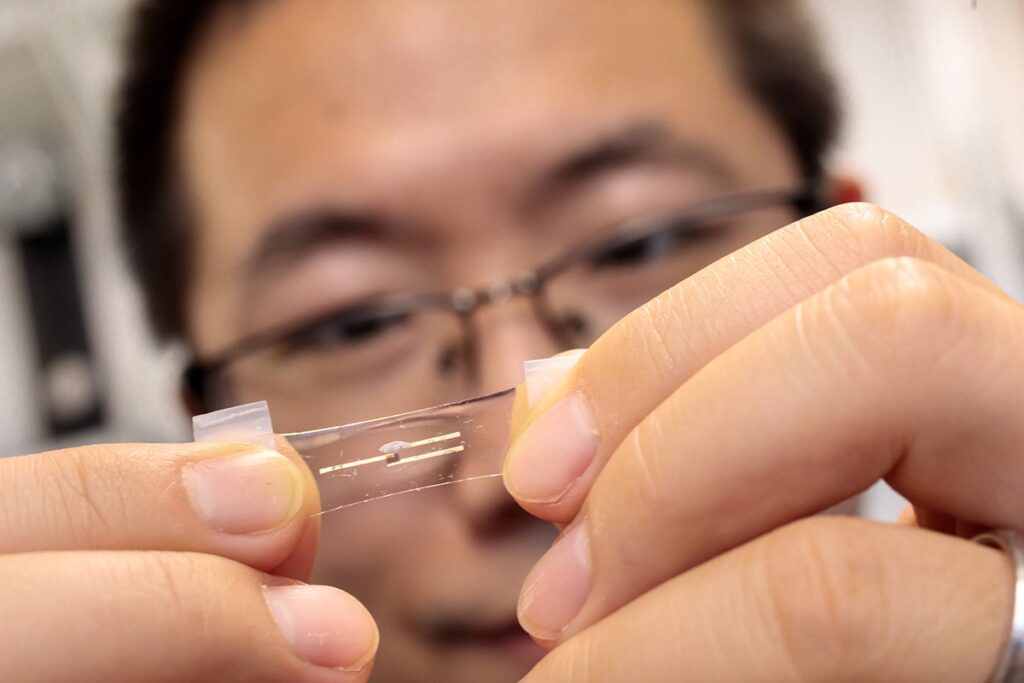
It’s a brainy Band-Aid, a smart watch without the watch, and a leap forward for wearable health technologies. Researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have developed a flexible, stretchable computing chip that processes information by mimicking the human brain. The device, described in the journal Matter, aims to change the way health data is processed.
“With this work we’ve bridged wearable technology with artificial intelligence and machine learning to create a powerful device which can analyze health data right on our own bodies,” said Sihong Wang, a materials scientist and Assistant Professor of Molecular Engineering.
Today, getting an in-depth profile about your health requires a visit to a hospital or clinic. In the future, Wang said, people’s health could be tracked continuously by wearable electronics that can detect disease even before symptoms appear. Unobtrusive, wearable computing devices are one step toward making this vision a reality.
A Data Deluge
The future of healthcare that Wang—and many others—envision includes wearable biosensors to track complex indicators of health including levels of oxygen, sugar, metabolites and immune molecules in people’s blood. One of the keys to making these sensors feasible is their ability to conform to the skin. As such skin-like wearable biosensors emerge and begin collecting more and more information in real-time, the analysis becomes exponentially more complex. A single piece of data must be put into the broader perspective of a patient’s history and other health parameters.Today’s smart phones are not capable of the kind of complex analysis required to learn a patient’s baseline health measurements and pick out important signals of disease. However, cutting-edge artificial intelligence platforms that integrate machine learning to identify patterns in extremely complex datasets can do a better job. But sending information from a device to a centralized AI location is not ideal.
“Sending health data wirelessly is slow and presents a number of privacy concerns,” he said. “It is also incredibly energy inefficient; the more data we start collecting, the more energy these transmissions will start using.”
Skin and Brains
Wang’s team set out to design a chip that could collect data from multiple biosensors and draw conclusions about a person’s health using cutting-edge machine learning approaches. Importantly, they wanted it to be wearable on the body and integrate seamlessly with skin.“With a smart watch, there’s always a gap,” said Wang. “We wanted something that can achieve very intimate contact and accommodate the movement of skin.”
Wang and his colleagues turned to polymers, which can be used to build semiconductors and electrochemical transistors but also have the ability to stretch and bend. They assembled polymers into a device that allowed the artificial-intelligence-based analysis of health data. Rather than work like a typical computer, the chip— called a neuromorphic computing chip—functions more like a human brain, able to both store and analyze data in an integrated way.
Testing the Technology
To test the utility of their new device, Wang’s group used it to analyze electrocardiogram (ECG) data representing the electrical activity of the human heart. They trained the device to classify ECGs into five categories—healthy or four types of abnormal signals. Then, they tested it on new ECGs. Whether or not the chip was stretched or bent, they showed, it could accurately classify the heartbeats.More work is needed to test the power of the device in deducing patterns of health and disease. But eventually, it could be used either to send patients or clinicians alerts, or to automatically tweak medications.
“If you can get real-time information on blood pressure, for instance, this device could very intelligently make decisions about when to adjust the patient’s blood pressure medication levels,” said Wang. That kind of automatic feedback loop is already used by some implantable insulin pumps, he added.
He already is planning new iterations of the device to both expand the type of devices with which it can integrate and the types of machine learning algorithms it uses.
“Integration of artificial intelligence with wearable electronics is becoming a very active landscape,” said Wang. “This is not finished research, it’s just a starting point.”
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Intrinsically stretchable neuromorphic devices for on-body processing of health data with artificial intelligence by Shilei Dai, Yahao Dai, Zixuan Zhao, Jie Xu, Jia Huang, Sihong Wang. Matter DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2022.07.016 Published: August 04, 2022
This paper is behind a paywall.