This is all at the microscale (for those who don’t know what micro means in this context, it’s one-millionth; specifically, the needles are measured in miilionths of a meter).
From a September 14, 2022 Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech) news release (also on EurekAlert),
Instead of sitting in a tattoo chair for hours enduring painful punctures, imagine getting tattooed by a skin patch containing microscopic needles. Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed low-cost, painless, and bloodless tattoos that can be self-administered and have many applications, from medical alerts to tracking neutered animals to cosmetics.
“We’ve miniaturized the needle so that it’s painless, but still effectively deposits tattoo ink in the skin,” said Mark Prausnitz, principal investigator on the paper. “This could be a way not only to make medical tattoos more accessible, but also to create new opportunities for cosmetic tattoos because of the ease of administration.”
Prausnitz, Regents’ Professor and J. Erskine Love Jr. Chair in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, presented the research in the journal iScience, with former Georgia Tech postdoctoral fellow Song Li as co-author.
Tattoos are used in medicine to cover up scars, guide repeated cancer radiation treatments, or restore nipples after breast surgery. Tattoos also can be used instead of bracelets as medical alerts to communicate serious medical conditions such as diabetes, epilepsy, or allergies.
Various cosmetic products using microneedles are already on the market — mostly for anti-aging — but developing microneedle technology for tattoos is new. Prausnitz, a veteran in this area, has studied microneedle patches for years to painlessly administer drugs and vaccines to the skin without the need for hypodermic needles.
“We saw this as an opportunity to leverage our work on microneedle technology to make tattoos more accessible,” Prausnitz said. “While some people are willing to accept the pain and time required for a tattoo, we thought others might prefer a tattoo that is simply pressed onto the skin and does not hurt.”
Transforming Tattooing
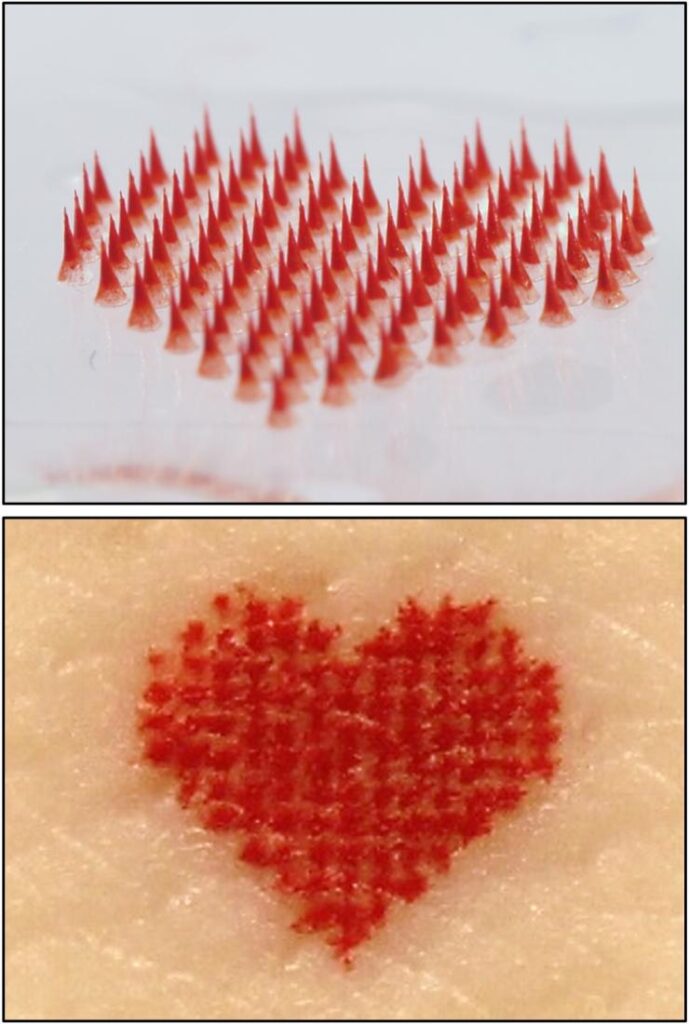
Tattoos typically use large needles to puncture repeatedly into the skin to get a good image, a time-consuming and painful process. The Georgia Tech team has developed microneedles that are smaller than a grain of sand and are made of tattoo ink encased in a dissolvable matrix.
“Because the microneedles are made of tattoo ink, they deposit the ink in the skin very efficiently,” said Li, the lead author of the study.
In this way, the microneedles can be pressed into the skin just once and then dissolve, leaving the ink in the skin after a few minutes without bleeding.
Tattooing Technique
Although most microneedle patches for pharmaceuticals or cosmetics have dozens or hundreds of microneedles arranged in a square or circle, microneedle patch tattoos imprint a design that can include letters, numbers, symbols, and images. By arranging the microneedles in a specific pattern, each microneedle acts like a pixel to create a tattoo image in any shape or pattern.
The researchers start with a mold containing microneedles in a pattern that forms an image. They fill the microneedles in the mold with tattoo ink and add a patch backing for convenient handling. The resulting patch is then applied to the skin for a few minutes, during which time the microneedles dissolve and release the tattoo ink. Tattoo inks of various colors can be incorporated into the microneedles, including black-light ink that can only be seen when illuminated with ultraviolet light.
Prausnitz’s lab has been researching microneedles for vaccine delivery for years and realized they could be equally applicable to tattoos. With support from the Alliance for Contraception in Cats and Dogs, Prausnitz’s team started working on tattoos to identify spayed and neutered pets, but then realized the technology could be effective for people, too.
The tattoos were also designed with privacy in mind. The researchers even created patches sensitive to environmental factors such as light or temperature changes, where the tattoo will only appear with ultraviolet light or higher temperatures. This provides patients with privacy, revealing the tattoo only when desired.
The study showed that the tattoos could last for at least a year and are likely to be permanent, which also makes them viable cosmetic options for people who want an aesthetic tattoo without risk of infection or the pain associated with traditional tattoos. Microneedle tattoos could alternatively be loaded with temporary tattoo ink to address short-term needs in medicine and cosmetics.
Microneedle patch tattoos can also be used to encode information in the skin of animals. Rather than clipping the ear or applying an ear tag to animals to indicate sterilization status, a painless and discreet tattoo can be applied instead.
“The goal isn’t to replace all tattoos, which are often works of beauty created by tattoo artists,” Prausnitz said. “Our goal is to create new opportunities for patients, pets, and people who want a painless tattoo that can be easily administered.”
Prausnitz has co-founded a company called Micron Biomedical that is developing microneedle patch technology, bringing it further into clinical trials, commercializing it, and ultimately making it available to patients.
Prausnitz and several other Georgia Tech researchers are inventors of the microneedle patch technology used in this study and have ownership interest in Micron Biomedical. They are entitled to royalties derived from Micron Biomedical’s future sales of products related to the research. These potential conflicts of interest have been disclosed and are overseen by Georgia Institute of Technology.
You can see what they mean when they claim this is not competitive with the work you’ll see from a tattoo artist,
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Microneedle patch tattoos by Song Li, Youngeun Kim, Jeong Woo Lee, Mark R. Prausnitz. iScience DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105014 Published: September 14, 2022
This paper is open access.
The company mentioned in the news release, Micron Biomedical can be found here.