Electrochromic windows hold great promise where energy savings are concerned. So far, it’s still just a promise but perhaps the research in this April 17, 2023 news item on phys.org will help realize it, Note: Links have been removed,
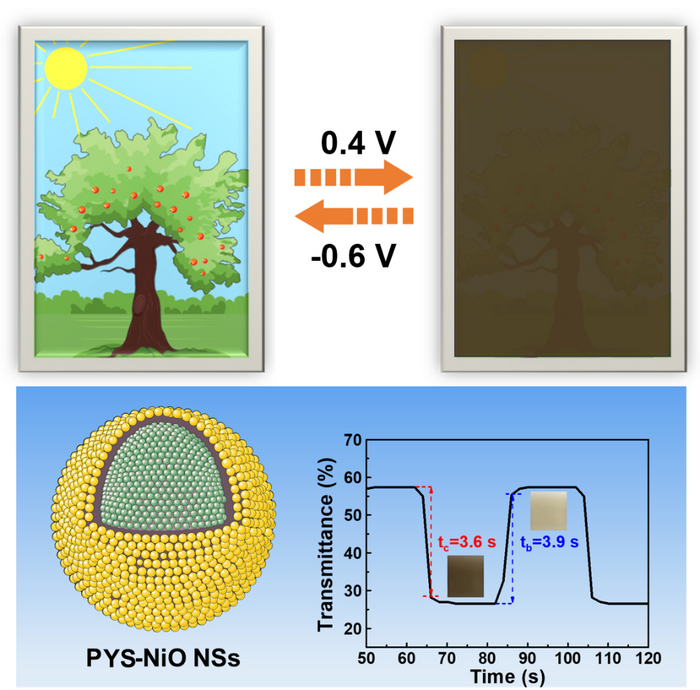
Researchers from Tsinghua University synthesized porous yolk-shell NiO nanospheres (PYS-NiO NSs) via a solvothermal and subsequent calcination process of Ni-MOF. As the large specific surface areas and hollow porous nanostructures were conducive to ionic transport, PYS-NiO NSs exhibited a fast coloring/bleaching speed (3.6/3.9 s per one coloring/bleaching cycle) and excellent cycling stability (82% of capacity retention after 3000 cycles). These superior electrochromic (EC) properties indicated that the PYS-NiO NSs was a promising candidate for high performance EC devices.
Electrochromic (EC) materials (ECMs) are defined as the materials which have reversible changes in their colors and optical properties (transmittance, reflectance, and absorption) under different external voltages. Over the past decades, ECMs show promising advantages and application prospects in many fields such as smart windows, adaptive camouflage, electronic displays, and energy storage, etc., because of their excellent optical modulation abilities.
…
This image doesn’t seem all that helpful (to me) in understanding the research,
An April 17, 2023 Particuology (journal) news release on EurekAlert, which originated the news item, does provide more detail, Note: Links have been removed,
Transition metal oxides (TMOs) are one of the most important ECMs which have been widely studied. They have many advantages such as rich nanostructure design, simple synthesis process, high security, etc. Among them, nickel oxide (NiO) is an attractive anode ECM and has attracted extensive research interest due to its high optical contrast, high coloring efficiency, low cost, etc. However, NiO-based ECMs still face the challenges of long EC switching times and poor cycling life which are caused by their poor ionic/electronic diffusion kinetics and low electrical conductivity.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted enormous attention, because of their high porosity and large surface areas, and could be adjusted to achieve different properties by selecting different metal ions and organic bridging ligands. Due to the porosity and long-range orderliness, MOFs can provide fast and convenient channels for small molecules and ions to insert and extract during the transformation process. Therefore, MOFs can be used as effective templates for the preparation of hollow and porous TMOs with high ion transport efficiency, excellent specific capacitance, and electrochemical activities.
So the authors proposed a new strategy to design a kind of NiO with hollow and porous structure to obtain excellent EC performance and cyclic stability. As a proof-of-concept demonstration, the authors successfully synthesized MOFs-derived porous yolk-shell NiO nanospheres (PYS-NiO NSs) which exhibited excellent EC performance. Ni-organic framework spheres were prepared by a simple solvothermal method and then converted to PYS-NiO NSs by thermal decomposition. The PYS-NiO NSs exhibited relatively high specific surface areas and stable hollow nanostructures, which not only provided a large contact area between active sites and electrolyte ions in the EC process but also helped the NiO to accommodate large volume changes without breaking. Besides, the PYS-NiO NSs also shortened the ionic diffusion length and provided efficient channels for transferring electronics and ions. In addition, the coupling with carbon also rendered the PYS-NiO NSs with improved electronic conductivity and obtained better EC performance. The PYS-NiO NSs exhibited a fast coloring/bleaching speed (3.6/3.9 s). Besides, PYS-NiO NSs also exhibited excellent cycling stability (82% of capacity retention after 3000 cycles). These superior EC properties indicate that the PYS-NiO NSs is a promising candidate for high-performance EC devices. The as-prepared PYS-NiO NSs are believed to be a promising candidate for smart windows, displays, antiglare rearview mirrors, etc. More importantly, this work provides a new and feasible strategy for the efficient preparation of ECMs with fast response speed and high cyclic stability.
Particuology (IF=3.251) is an interdisciplinary journal that publishes frontier research articles and critical reviews on the discovery, formulation and engineering of particulate materials, processes and systems. Topics are broadly relevant to the production of materials, pharmaceuticals and food, the conversion of energy resources, and protection of the environment. For more information, please visit: https://www.journals.elsevier.com/particuology.
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper, Note: There is an unusually long lead time between online access and print access,
Novel self-assembled porous yolk-shell NiO nanospheres with excellent electrochromic performance for smart windows by Baoshun Wang, Ya Huang, Siming Zhao, Run Li, Di Gao, Hairong Jiang, Rufan Zhang. Particuology Volume 84, January 2024, Pages 72-80 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2023.03.007 Available online: April 17, 2023
This paper is open access.