h/t to Miriam Halpenny’s October 14, 2019 Castanet article as seen on the Vancouverisawesome website for this news about bulletproof clothing being developed for Canada’s National Department of Defence. I found a September 4, 2019 University of British Columbia Okanagan news release describing the research and the funds awarded to it,
The age-old technique of dressing in layers is a tried and tested way to protect from the elements. Now thanks to $1.5 million in new funding for UBC’s Okanagan campus, researchers are pushing the practice to new limits by creating a high-tech body armour solution with multiple layers of protection against diverse threats.
“Layers are great for regulating body heat, protecting us from inclement weather and helping us to survive in extreme conditions,” says Keith Culver, director of UBC’s Survive and Thrive Applied Research (STAR) initiative, which is supporting the network of researchers who will be working together over the next three years. “The idea is to design and integrate some of the most advanced fabrics and materials into garments that are comfortable, practical and can even stop a bullet.”
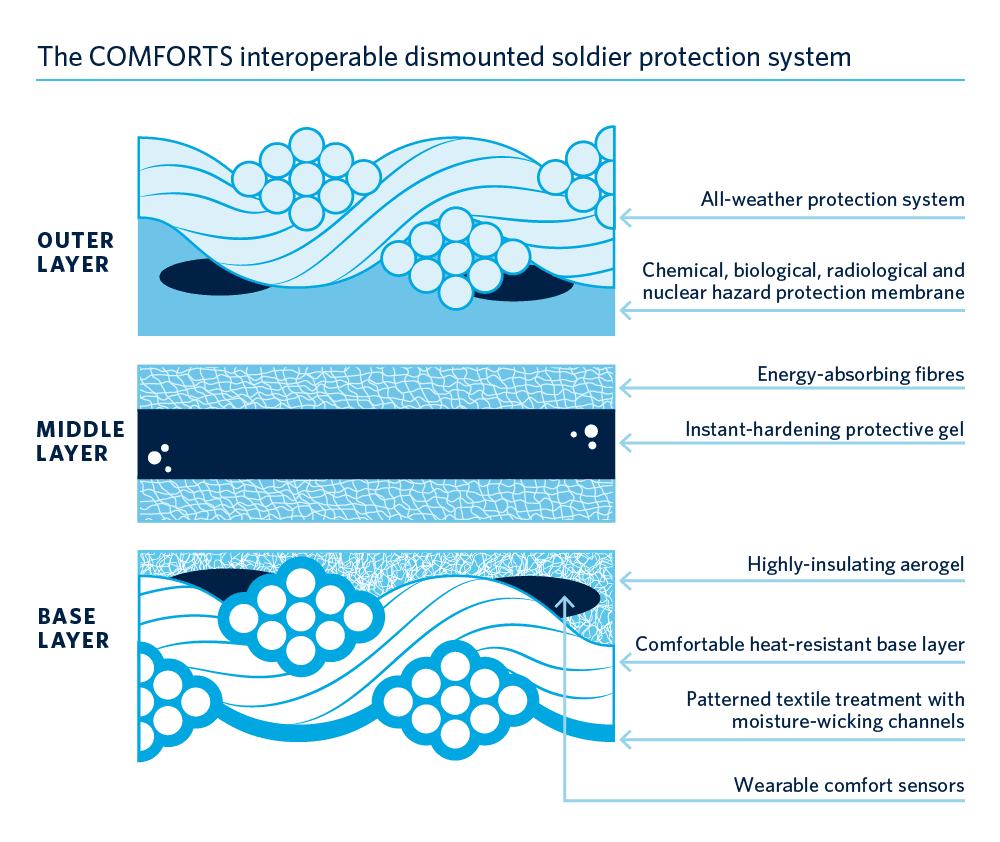
The research network working to develop these new Comfort-Optimized Materials For Operational Resilience, Thermal-transport and Survivability (COMFORTS) aims to create a futuristic new body armour solution by combining an intelligent, moisture-wicking base layer that has insulating properties with a layer of lightweight, ballistic-resistant material using cross-linker technology. It will also integrate a water, dust and gas repellent outer layer and will be equipped with comfort sensors to monitor the wearer’s response to extreme conditions.
“Although the basic idea seems simple, binding all these different materials and technologies together into a smart armour solution that is durable, reliable and comfortable is incredibly complex,” says Kevin Golovin, assistant professor of mechanical engineering at UBCO and principal investigator of the COMFORTS research network. “We’re putting into practice years of research and expertise in materials science to turn the concept into reality.”
The COMFORTS network is a collaboration between the University of British Columbia, the University of Alberta and the University of Victoria and is supported by a number of industrial partners. The network has received a $1.5M contribution agreement from the Department of National Defence through its Innovation for Defence Excellence and Security (IDEaS) program, designed to support innovation in defence and security.
“The safety and security threats faced by our military are ever-changing,” says Culver. “Hazards extend beyond security threats from foreign forces to natural disasters now occurring more frequently than ever before. Almost every year we’re seeing natural disasters, forest fires and floods that put not just ordinary Canadians at risk but also the personnel that respond directly to those threats. Our goal is to better protect those who put their lives on the line to protect the rest of us.”
While the initial COMFORTS technologies developed will be for defence and security applications, Culver says the potential extends well beyond the military.
“Imagine a garment that could keep its users comfortable and safe as they explore the tundra of the Canadian arctic, fight a raging forest fire or respond to a corrosive chemical spill,” says Culver. “I imagine everyone from first responders to soldiers to extreme athletes being impacted by this kind of innovation in protective clothing.”
The research will be ongoing with eight projects planned over the next three years. Some of the protective materials testing will take place at UBC’s STAR Impact Research Facility (SIRF), located just north of UBC’s Okanagan campus. The ballistic and blast simulation facility is the only one of its kind in Canada—it supports research and testing of ballistic and blast-resistant armour, ceramic and other composite materials, as well as helmets and other protective gear.
“I anticipate we will see some exciting new, field-tested technologies developed within the next few years,” says Culver. “I look forward to seeing where this collaboration will lead us.”
To learn more about the COMFORTS project, visit: ok.ubc.ca/okanagan-stories/textile-tech
UBC Expert Q&A
Western Canada primed to be defense and security research hotspot
World-class vineyards and sunny lakeside resorts have long been the reputation for BC’s Okanagan Valley. That reputation has expanded with Kelowna’s growth as a tech hub, according to Professor Keith Culver, director of UBC’s Survive and Thrive Research (STAR) initiative, but core expertise in defense and security research has also been rapidly expanding since UBC launched the STAR initiative five years ago.
Culver is a professor, legal theorist, self-described convener and coach with proven expertise assembling multi-disciplinary research teams working at the vanguard of innovation. One of these teams, led by Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering Kevin Golovin, was recently awarded a $1.5 million contract by the Department of National Defense to develop next-generation, high-performance body armour that increases the safety and comfort of Canadian soldiers.
What is UBC’s STAR initiative?
UBC STAR is a group of researchers and partners working together to solve human performance challenges. We know that solving complex problems requires a multi-disciplinary approach, so we build teams with specialized expertise from across both our campuses and other Western Canadian universities. Then we blend that expertise with the know-how and production capabilities of private and public sector partners to put solutions into practice. Above all, STAR helps university researchers and partners to work together in new, more productive ways.
You recently received considerable new funding from the Department of National Defence. Can you tell us about that research
A team of researchers from UBC, the University of Alberta and the University of Victoria have established a research network to invent and test new materials for the protection of humans operating in extreme environments – in this case, soldiers doing their jobs on foot. Assistant Professor Kevin Golovin of UBC Okanagan’s School of Engineering is leading the network with support from UBC STAR. The network brings together three leading Western Canadian universities to work together with industry to develop new technologies for the defence and security sector.
The network is developing several kinds of protective materials and hazard sensors for use in protective armour for soldiers and first responders. The name of the network captures its focus nicely: Comfort-Optimized Materials For Operational Resilience, Thermal-transport and Survivabilty (COMFORTS). Researchers in engineering, chemistry and other disciplines are developing new textile technologies and smart armour solutions that will be rigorously tested for thermal resistance to increase soldier comfort. We’re fortunate to be working with a great group of companies ready to turn our research into solutions ready for use. We’ll help to solve the challenges facing Canadian first responders and soldiers while enabling Canadian companies to sell those solutions to international markets.
What does the safety and security landscape look like in Western Canada?
I think there’s a perception out there that this kind of research is only happening in places like Halifax, Toronto or Waterloo. Western Canadian expertise is sometimes overlooked by Ottawa and Toronto, but there’s incredible expertise and cutting-edge research happening here in the west, and we are fortunate to have a strong private sector partner community that understands safety and security problems in military contexts, and in forestry, mining and wildfire and flood response. Our understanding of hazardous environments gives us a head start in putting technologies and strategies to work safely in extreme conditions, and we’re coming to realize that our creative solutions can both help Canadians and others around the world.
Why do companies want to work with UBC STAR and its Western Canadian partners?
We have great researchers and great facilities – our blast simulator and ballistics range are second to none – but we offer much more than expertise and equipment. UBC STAR is fundamentally about making the most of collaboration. We work together with our partners to understand the nature of problems and what could contribute to a solution. We readily draw on expertise from multiple universities and firms to assemble the right team. And we know that we are in the middle of a great living lab for testing solutions –with rural and urban areas of varying sizes, climates and terrains. We’re situated in an ideal place to work through technology development, while identifying the strategies and standards needed to put innovative technology to good use.
How do you expect this sector to develop over the next decade?
I see a boom coming in this sector. In Canada, and around the world, we are witnessing a rise in natural disasters that put first responders and others at risk, and our research can help improve their safety. At the same time, we are seeing a rise in global political tensions calling for Canadian military deployment in peacekeeping and other support roles. Our military needs help protecting its members so they can do their jobs in dangerous places. And, of course, when we develop protective materials for first responders and soldiers, the same solutions can be easily adapted for use in sport and health – such as protecting children playing contact sports or our aging population from slip and fall injuries. I think I speak for everyone involved in this research when I say that it’s incredibly rewarding to see how solutions found addressing one question often have far broader benefits for Canadians in every walk of life.
To learn more about STAR, visit: star.ubc.ca
About UBC’s Okanagan campus
UBC’s Okanagan campus is an innovative hub for research and learning in the heart of British Columbia’s stunning Okanagan Valley. Ranked among the top 20 public universities in the world, UBC is home to bold thinking and discoveries that make a difference. Established in 2005, the Okanagan campus combines a globally recognized UBC education with a tight-knit and entrepreneurial community that welcomes students and faculty from around the world.
To find out more, visit: ok.ubc.ca
I have mentioned* bulletproof clothing here in a November 4, 2013 posting featuring a business suit that included carbon nanotubes providing protection from bullets. Here’s where you can order one.
*’mentioned’ was substituted for ‘featured’ as a grammar correction on July 6, 2020.