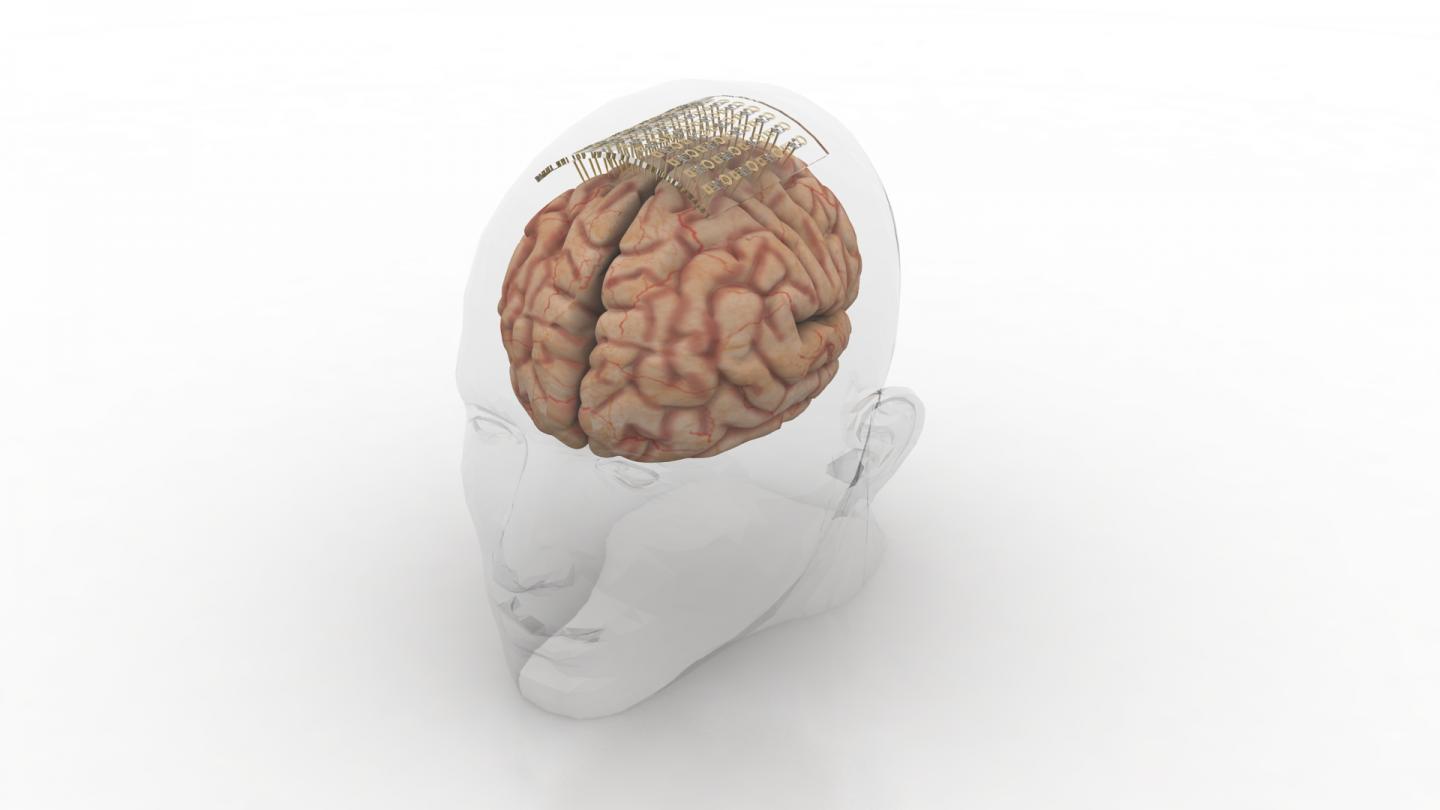
I have two news bits (dated almost one month apart) about the use of graphene in neural probes, one from the European Union and the other from Korea.
European Union (EU)
This work is being announced by the European Commission’s (a subset of the EU) Graphene Flagship (one of two mega-funding projects announced in 2013; 1B Euros each over ten years for the Graphene Flagship and the Human Brain Project).
According to a March 27, 2017 news item on ScienceDaily, researchers have developed a graphene-based neural probe that has been tested on rats,
Measuring brain activity with precision is essential to developing further understanding of diseases such as epilepsy and disorders that affect brain function and motor control. Neural probes with high spatial resolution are needed for both recording and stimulating specific functional areas of the brain. Now, researchers from the Graphene Flagship have developed a new device for recording brain activity in high resolution while maintaining excellent signal to noise ratio (SNR). Based on graphene field-effect transistors, the flexible devices open up new possibilities for the development of functional implants and interfaces.
The research, published in 2D Materials, was a collaborative effort involving Flagship partners Technical University of Munich (TU Munich; Germany), Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS; Spain), Spanish National Research Council (CSIC; Spain), The Biomedical Research Networking Center in Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN; Spain) and the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2; Spain).
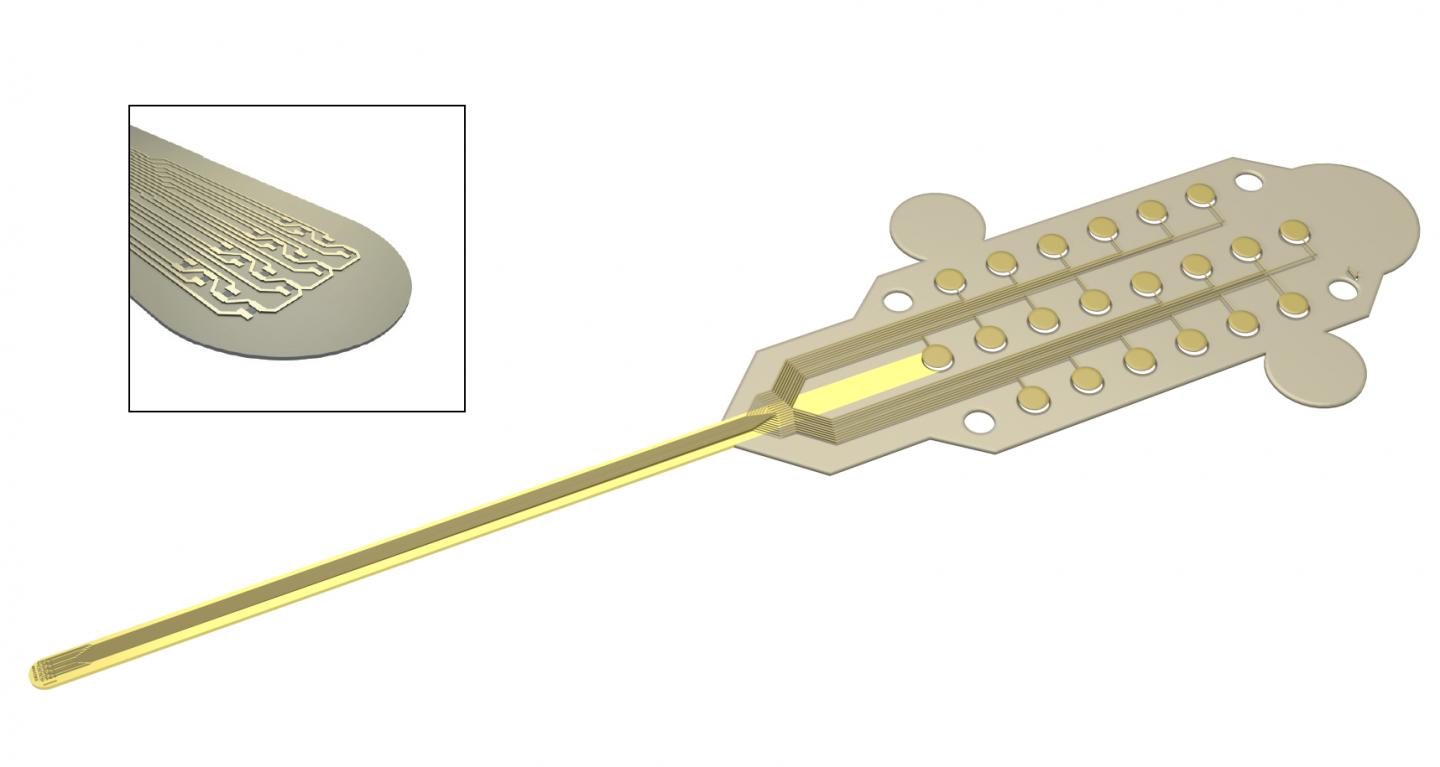
Caption: Graphene transistors integrated in a flexible neural probe enables electrical signals from neurons to be measured with high accuracy and density. Inset: The tip of the probe contains 16 flexible graphene transistors. Credit: ICN2
A March 27, 2017 Graphene Flagship press release on EurekAlert, which originated the news item, describes the work, in more detail,
The devices were used to record the large signals generated by pre-epileptic activity in rats, as well as the smaller levels of brain activity during sleep and in response to visual light stimulation. These types of activities lead to much smaller electrical signals, and are at the level of typical brain activity. Neural activity is detected through the highly localised electric fields generated when neurons fire, so densely packed, ultra-small measuring devices is important for accurate brain readings.
The neural probes are placed directly on the surface of the brain, so safety is of paramount importance for the development of graphene-based neural implant devices. Importantly, the researchers determined that the graphene-based probes are non-toxic, and did not induce any significant inflammation.
Devices implanted in the brain as neural prosthesis for therapeutic brain stimulation technologies and interfaces for sensory and motor devices, such as artificial limbs, are an important goal for improving quality of life for patients. This work represents a first step towards the use of graphene in research as well as clinical neural devices, showing that graphene-based technologies can deliver the high resolution and high SNR needed for these applications.
First author Benno Blaschke (TU Munich) said “Graphene is one of the few materials that allows recording in a transistor configuration and simultaneously complies with all other requirements for neural probes such as flexibility, biocompability and chemical stability. Although graphene is ideally suited for flexible electronics, it was a great challenge to transfer our fabrication process from rigid substrates to flexible ones. The next step is to optimize the wafer-scale fabrication process and improve device flexibility and stability.”
Jose Antonio Garrido (ICN2), led the research. He said “Mechanical compliance is an important requirement for safe neural probes and interfaces. Currently, the focus is on ultra-soft materials that can adapt conformally to the brain surface. Graphene neural interfaces have shown already great potential, but we have to improve on the yield and homogeneity of the device production in order to advance towards a real technology. Once we have demonstrated the proof of concept in animal studies, the next goal will be to work towards the first human clinical trial with graphene devices during intraoperative mapping of the brain. This means addressing all regulatory issues associated to medical devices such as safety, biocompatibility, etc.”
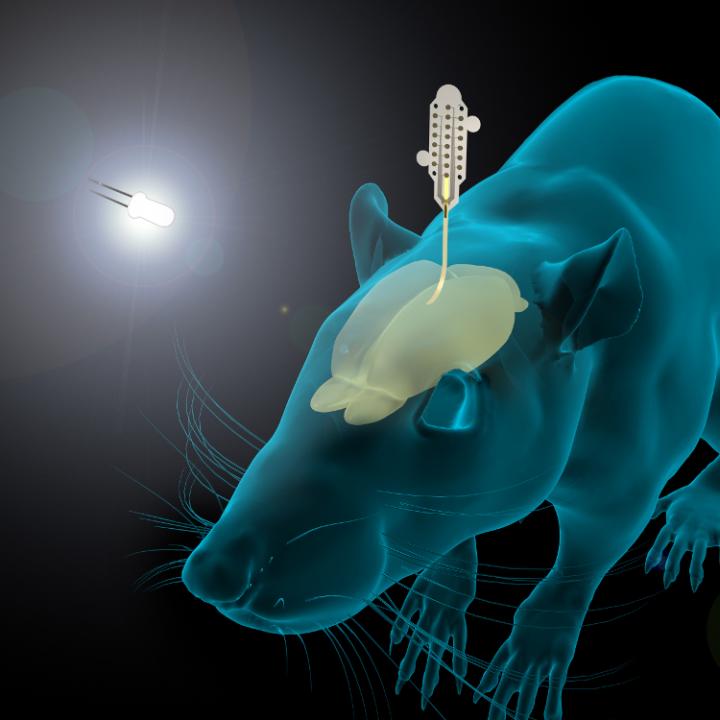
Caption: The graphene-based neural probes were used to detect rats’ responses to visual stimulation, as well as neural signals during sleep. Both types of signals are small, and typically difficult to measure. Credit: ICN2
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Mapping brain activity with flexible graphene micro-transistors by Benno M Blaschke, Núria Tort-Colet, Anton Guimerà-Brunet, Julia Weinert, Lionel Rousseau, Axel Heimann, Simon Drieschner, Oliver Kempski, Rosa Villa, Maria V Sanchez-Vives. 2D Materials, Volume 4, Number 2 DOI https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/aa5eff Published 24 February 2017
© 2017 IOP Publishing Ltd
This paper is behind a paywall.
Korea
While this research from Korea was published more recently, the probe itself has not been subjected to in vivo (animal testing). From an April 19, 2017 news item on ScienceDaily,
Electrodes placed in the brain record neural activity, and can help treat neural diseases like Parkinson’s and epilepsy. Interest is also growing in developing better brain-machine interfaces, in which electrodes can help control prosthetic limbs. Progress in these fields is hindered by limitations in electrodes, which are relatively stiff and can damage soft brain tissue.
Designing smaller, gentler electrodes that still pick up brain signals is a challenge because brain signals are so weak. Typically, the smaller the electrode, the harder it is to detect a signal. However, a team from the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology [DGIST} in Korea developed new probes that are small, flexible and read brain signals clearly.
This is a pretty interesting way to illustrate the research,
An April 19, 2017 DGIST press release (also on EurekAlert), which originated the news item, expands on the theme (Note: A link has been removed),
The probe consists of an electrode, which records the brain signal. The signal travels down an interconnection line to a connector, which transfers the signal to machines measuring and analysing the signals.
The electrode starts with a thin gold base. Attached to the base are tiny zinc oxide nanowires, which are coated in a thin layer of gold, and then a layer of conducting polymer called PEDOT. These combined materials increase the probe’s effective surface area, conducting properties, and strength of the electrode, while still maintaining flexibility and compatibility with soft tissue.
Packing several long, thin nanowires together onto one probe enables the scientists to make a smaller electrode that retains the same effective surface area of a larger, flat electrode. This means the electrode can shrink, but not reduce signal detection. The interconnection line is made of a mix of graphene and gold. Graphene is flexible and gold is an excellent conductor. The researchers tested the probe and found it read rat brain signals very clearly, much better than a standard flat, gold electrode.
“Our graphene and nanowires-based flexible electrode array can be useful for monitoring and recording the functions of the nervous system, or to deliver electrical signals to the brain,” the researchers conclude in their paper recently published in the journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
The probe requires further clinical tests before widespread commercialization. The researchers are also interested in developing a wireless version to make it more convenient for a variety of applications.
Here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Enhancement of Interface Characteristics of Neural Probe Based on Graphene, ZnO Nanowires, and Conducting Polymer PEDOT by Mingyu Ryu, Jae Hoon Yang, Yumi Ahn, Minkyung Sim, Kyung Hwa Lee, Kyungsoo Kim, Taeju Lee, Seung-Jun Yoo, So Yeun Kim, Cheil Moon, Minkyu Je, Ji-Woong Choi, Youngu Lee, and Jae Eun Jang. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9 (12), pp 10577–10586 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b02975 Publication Date (Web): March 7, 2017
Copyright © 2017 American Chemical Society
This paper is behind a paywall.