The euphoria is dying down and, on balance, there was surprisingly little, the tone being more one of optimism laced with caution on the occasion of the Conservative’s defeat at the hands of the Liberal party in the Oct. 19, 2015 Canadian federal election.
Of course the big question for me and other Canadian science bloggers is:
What about science in the wake of the 2015 Liberal majority government in Canada?
I’ve gathered bits and pieces from various published opinions on the topic. First, there’s Brian Owen, a freelance writer in St. Stephen, New Brunswick (there’s more about him in my Aug. 18, 2015 posting about the upcoming Canadian Science Policy Conference to be held Nov. 25 -27, 2015 in Ottawa [Canada’s capital]) in an Oct. 20, 2015 opinion piece for ScienceInsider,
Many Canadian scientists are celebrating the result of yesterday’s federal election, which saw Stephen Harper’s Conservative government defeated after nearly 10 years in power.
The center-left Liberal Party under Justin Trudeau won an unexpected majority government, taking 184 of the 338 seats in the House of Commons. The Conservatives will form the opposition with 99 seats, while the left-leaning New Democratic Party (NDP) fell to third place with just 44 seats.
“Many scientists will be pleased with the outcome,” says Jim Woodgett, director of research at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto. “The Liberal party has a strong record in supporting science.” [emphasis mine]
I don’t think the Liberal record is that great. If I understand it rightly, the first muzzle placed on government scientists was applied by a then Liberal government to Health Canada. That’s right the Conservatives got the idea from the Liberals and it’s not the only one they got from that source. Omnibus bills were also pioneered by the Liberal government.
However, hope still springs in mine and others’ bosoms as can be seen in an Oct. 21, 2015 essay in the Guardian (UK newspaper) by Michael Halpern of the Center for Science and Democracy at the US-based Union of Concerned Scientists (Note: Links have been removed),
There was a palpable outpouring of relief from Canadian scientists as the Liberal Party won a majority on Monday night [Oct. 19, 2015], bringing to an end nine years of escalating hostility by the Harper government towards its own research base. Drastic cuts to funding and constraints on scientific freedom have significantly damaged Canadian research and its capacity to develop science-based public health and environmental policies.
…
Eight hundred scientists from thirty-two countries wrote an open letter urging the prime minster to ease restrictions on scientists and data. In October 2014, a Ryerson University professor wrote in Science magazine that the election presented an “opportunity to reboot the federal government’s controversial approach to science policy and research.”
All of this advocacy worked. Science became a major campaign issue during the election. There were all-party debates on science policy and extensive media coverage. The Green, Liberal and NDP platforms included significant commitments to restore science to its rightful place in society and public policy.
“We’ll reverse the $40 million cut that Harper made to our federal ocean science and monitoring programs,” said Liberal leader Justin Trudeau at a September campaign stop. “The war on science ends with the liberal government.” In tweet after tweet after tweet, opposition candidates argued that they were best positioned to defend scientific integrity.
Now that it’s been elected with a healthy majority, the Liberal Party says it will make data openly available, unmuzzle scientists, bring back the long form census, appoint a chief science officer, and make the agency Statistics Canada fully independent.
In the United States, many celebrated the end of the Bush administration in 2008, thinking that its restrictions on science would evaporate the moment that the Obama administration took office. It wasn’t true. There has been significant progress in protecting scientists from political influence. But the public has still lacked access to scientific information on multiple environmental and public health issues.
So who will keep watch over the new government, as it’s forced to choose among its many priorities? Canadian unions, scientists, policy experts and activists need to continue to push for real change. It’s up to those who care most about science and democracy to keep Trudeau on his toes.
Returning to Owen’s article, there are more pledges from the new Liberal government,
… Trudeau has also said his party will embrace “evidence based policy” and “data-driven decision-making,” do more to address climate change, protect endangered species, and review the environmental impact of major energy and development projects.
Woodgett welcomes those pledges, but warns that they would not address the larger issue of what he sees as the government’s neglect of basic research funding. “I hope we will see less short-term thinking and much greater support for discovery research going forward,” he says. “We are at serious risk of a lost generation of scientists and it’s critical that younger researchers are given a clear indication that Canada is open to their ideas and needs.”
Science advocates plan to watch the new government closely to ensure it lives up to its promises. “Great to see Harper gone, but another majority is an awfully big blank cheque,” wrote Michael Rennie, a freshwater ecologist at Lakehead University in Thunder Bay, on Twitter.
David Bruggeman in a cautionary Oct. 22, 2015 posting (on his Pasco Phronesis blog) sums things up in this title: Will New Canadian Government Be The Change Its Scientists Can Believe In? (Note: Links have been removed),
… Only one of the four party representatives at the recent science and technology debate managed to win a seat in the upcoming Parliament. MP Marc Garneau will remain in Parliament, and his experience in the Canadian Space Agency means he may be able to better manage the changes sought in official government (as opposed to Parliamentary) policy.
The Conservatives will now shift to being the Official Opposition (the largest party not in power). However, the current cabinet minister responsible for science and technology, and at least two of his predecessors, lost their seats. The party that was the Official Opposition, the New Democratic Party (NDP), lost several seats, returning to the third largest party in Parliament. (However, they appear to be a more natural ally for the Liberals than the Conservatives) MP Kennedy Stewart, who has championed the establishment of a Parliamentary Science Officer, barely retained his seat. He will likely remain as the NDP science critic.
… While the policies on media access to government scientists are part of this trend, they may not be the first priority for Trudeau and his cabinet. It may turn out to be something similar to the transition from the Bush to the Obama Administrations. Changes to policies concerning so-called political interference with science were promised, but have not gotten the thorough commitment from the Obama Administration that some would have liked and/or expected.
As David notes. we lost significant critical voices when those Conservative MPs failed to get re-elected.
In a post-election Oct. 24, 2015 posting, Sarah Boon offers a call to action on her Watershed Moments blog (Note: Links have been removed),
I think it’s important to realize, however, that the work doesn’t end here.
Canadian scientists found their voice in the run up to the election, but they’d better not lose it now.
In a pre-election editorial on the Science Borealis Blog, Pascal Lapointe suggested that – after the election – the organizations that worked so hard to make science an election issue should join forces and keep pushing the government to keep science as a top priority. These groups include Evidence for Democracy, the Science Integrity Project, Get Science Right, Our Right to Know, the Professional Institute of the Public Service of Canada, and more.
Finally, there’s an Oct. 20, 2015 posting by Canadians Julia Whidden and Rachel Skubel on the Southern Fried Science blog explaining the Canadian election to American colleagues in what begins in a facey style which, thankfully and quickly, switches to informative and opinionated (Note: They have nothing good to say about the Conservatives and science),
Up until this past year, the thought of Canadian politics had probably never crossed your mind. For some of you, your introduction to the topic may have been via the astute criticisms of John Oliver published this past weekend. His YouTube video currently skyrocketing at just under 3 million views in less than 48 hours, may have even been the introduction to Canadian politics for some Canadians. Let’s face it: in comparison to the flashy and sometimes trashy race of our neighbors to the south (ahem, you Americans), Canadian politics are usually tame, boring, and dry. …
…
We present a few major issues related to marine science and conservation that Harper either dragged down or destroyed, and the complementary response by our new PM Trudeau from his platform. …
…
Based on the Liberals party’s platform, and their statements throughout the last year, here’s a taste of the contrasts between old and new:
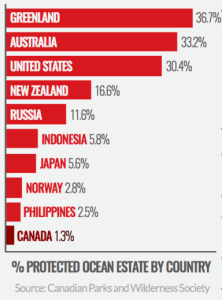
Harper/Conservatives Trudeau/Liberals Marine Protected AreasCommitted in 2011 to protect 10% of Canada’s coastal marine and coastal areas by 2020 under the International Convention on Biodiversity, but is lagging at a meager 1.3% – and only 0.11% is fully closed to “extractive activities.”
Proposed MPAs have been stalled by inaction, failure to cooperate by the federal government or stakeholders, and overall a system which needs an infusion of resources – not cuts – to meet ambitious goals.
“We will increase the amount of Canada’s marine and coastal areas that are protected from 1.3 percent to 5 percent by 2017, and 10 percent by 2020.” Liberal Party’s Protecting our Oceans mandate
There is a bit of misinformation in the Southern Fried Science posting,
The National Research Council (NRC) is Canada’s equivalent of America’s National Science Foundation (NSF).
The closest analogue to the US National Science Foundation is Canada’s Tri-Council Agencies comprised of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC), the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC), and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR).
Next step: appointing a cabinet
Oddly, I haven’t found anyone speculating as to what will happen to science when Justin Trudeau announces his cabinet. He has already stated that his cabinet will be significantly smaller than Stephen Harper’s cabinet of 39 ministers. Numbers for the new cabinet range from 25 to 28 to 30. The largest proposed Trudeau cabinet (30) is almost 25% less than the previous one. Clearly, some ministries will have to go or be combined with other ones.
I’m guessing that Science, which is considered a junior ministry, will be rolled into another ministry, possibly Industry, to be renamed, Industry and Science. Or, by appointing a Chief Science Advisor, Trudeau trumpets the new importance of science with this special status and disburses the Science Ministry responsibilities amongst a variety of ministries.
In any event, I look forward to finding out later this week (Nov. 2 – 6, 2015) whether either or neither of my predictions comes true.
*Canadian cabinet update: To see how I got it both wrong and right see my Nov.4, 2015 posting.
ETA Nov. 5, 2015: I found one more piece for this roundup, an Oct. 22, 2015 article by Helen Carmichael for Chemistry World published by the UK’s Royal Society of Chemistry (Note: Links have been removed),
There will likely be a shift in the Canadian government’s target research areas towards areas such as green energy and away from fossil fuels, observers say. In addition, they expect that the Trudeau government will be more hands off when it comes to the science that it funds – giving money to the granting councils and trusting them to disburse those funds via peer review. …
The way that science is funded – the politicisation of science – will be less of an issue for the next while,’ says John Brennan, a chemistry and chemical biology professor at McMaster University in Ontario, Canada, who directs the school’s Biointerfaces Institute.
Trudeau and his Liberal party have promised to appoint a chief science officer similar to the national science adviser position that the Harper government eliminated in 2008. Canada’s new chief science officer would report to the prime minister and ensure that government science is available to the public, that all the country’s scientists are able to speak freely about their work and that scientific analyses are considered when the Canadian government develops policy. The Trudeau government has also said that it will create a central online portal for government-funded scientific research to enable greater public access.
…
The Liberals offer quite a different vision for the Canadian economy than the Conservatives, planning to run short-term budget deficits to increase government spending on public infrastructure, and to return the country to a balanced budget in 2019–20. The party has committed to C$25 million (£12 million) in funding for National Parks and reversing budget cuts to government ocean science and monitoring programmes.
In addition to proposing initiatives to increase business investment in research and development, the Liberals want a tax credit, and will invest C$200 million annually to support innovation in the forestry, fisheries, mining, energy and agriculture sectors. Public science is particularly important in Canada, where the private sector funds a much lower proportion of research than most industrialised nations.
…
Provincial governments own Canada’s natural resources, with fossil fuel production largely in Alberta and Saskatchewan. Energy production is a major part of the Canadian economy. Trudeau has committed to set up a C$2 billion fund to help the country transition to a low carbon economy, but meanwhile he is not expected to withdraw support for the proposed Alberta to Texas Keystone XL oil pipeline.
…
Incoming president and chief executive of the Chemistry Industry Association of Canada (CIAC), Bob Masterson, recently told Chemistry World that rapid policy decisions by Canadian governments and retailers, without sufficient consultation with industry, are not advantageous or based on sound science. He described missed opportunities for the Canadian chemical industry to engage with regulators, coupled with a lack of coordination between various tiers of Canada’s national and regional regulations. On key issues, such as Canada’s Chemical Management Plan, global trade and maintaining competitive corporate tax rates, Masterson says the CIAC believes the liberal positions represent continuity rather than change from the previous government.
Carmichael’s offers a good overview and is the only one of *three* (the others* being from David Bruggeman *and Michael Halpern*) analyses I’ve found, that are being written by people who are not navel gazing.
*’two’ changed to ‘three’, ‘other’ changed to ‘others’, and ‘and Michael Halpern’ added 1250 PST on Nov. 5, 2015.