This is a going to a science policy heavy posting with both a conference and the latest report from the Canadian Council of Academies (CCA).
2018 Canadian Science Policy Conference
As I noted in my March 1, 2018 posting, this is the fourth year in a row that the conference is being held in Ottawa and the theme for this 10th edition is ‘Building Bridges Between Science, Policy and Society‘.
The dates are November 7 -9, 2018 and as the opening draws closer I’m getting more ‘breathlessly enthusiastic’ announcements. Here are a few highlights from an October 23, 2018 announcement received via email,
CSPC 2018 is honoured to announce that the Honourable Kirsty Duncan, Minister of Science and Sport, will be delivering the keynote speech of the Gala Dinner on Thursday, November 8 at 7:00 PM. Minister Duncan will also hand out the 4th Science Policy Award of Excellence to the winner of this year’s competition.
…
CSPC 2018 features 250 speakers, a record number, and above is the breakdown of the positions they hold, over 43% of them being at the executive level and 57% of our speakers being women.
*All information as of October 15, 2018
…
If you think that you will not meet any new people at CSPC and all of the registrants are the same as last year, think again!
Over 57% of registrants are attending the conference for the FIRST TIME!
Secure your spot today!
*All information as of October 15, 2018
Here’s more from an October 31, 2018 announcement received via email,
One year after her appointment as Canada’s Chief Science Advisor, Dr. Mona Nemer will discuss her experience with the community. Don’t miss this opportunity.
…
[Canadian Science Policy Centre editorials in advance of conference]
Paul Dufour
“Evidence and Science in Parliament–Looking Back at CSPC and Moving Forward”Dr. Tom Corr
“Commercializing Innovation in Canada: Advancing in the Right Direction”Joseph S Sparling, PhD
“Reimagining the Canadian Postdoctoral Training System”Milton Friesen
“Conspiring Together for Good: Institutional Science and Religion”Joseph Tafese
“Science and the Next Generation : Science and Inclusivity, Going beyond the Slogans”Eva Greyeyes
“Opinion Editorial for CSPC, November 2018”Monique Crichlow
Chris Loken
“Policy Considerations Towards Converged HPC-AI Platforms”…
Should you be in the Ottawa area November 7 – 9, 2018, it’s still possible to register.
**Update November 6, 2018: The 2018 CSPC is Sold Out!**
Council of Canadian Academies: job and the ‘managing innovation’ report
Let’s start with the job (from the posting),
October 17, 2018Role Title: Director of Communications
Deadline: November 5, 2018
Salary: $115,000 to $165,000About the Council of Canadian Academies
The Council of Canadian Academies (CCA) is a not-for-profit organization that conducts assessments of evidence on scientific topics of public interest to inform decision-making in Canada.Role Summary
The CCA is seeking an experienced communications professional to join its senior management team as Director of Communications. Reporting to the President and CEO, the Director is responsible for developing and implementing a communications plan for the organization that promotes and highlights the CCA’s work, brand, and overall mission to a variety of potential users and stakeholders; overseeing the publication and dissemination of high-quality hard copy and online products; and providing strategic advice to the President and CCA’s Board, Committees, and Panels. In fulfilling these responsibilities, the Director of Communications is expected to work with a variety of interested groups including the media, the broad policy community, government, and non-governmental organizations.Key Responsibilities and Accountabilities
Under the direction of the President and CEO, the Director leads a small team of communications and publishing professionals to meet the responsibilities and accountabilities outlined below.Strategy Development and External Communications
• Develop and execute an overall strategic communications plan for the organization that promotes and highlights the CCA’s work, brand, and overall mission.
• Oversee the CCA’s presence and influence on digital and social platforms including the development and execution of a comprehensive content strategy for linking CCA’s work with the broader science and policy ecosystem with a focus on promoting and disseminating the findings of the CCA’s expert panel reports.
• Provide support, as needed for relevant government relations activities including liaising with communications counterparts, preparing briefing materials, responding to requests to share CCA information, and coordinating any appearances before Parliamentary committees or other bodies.
• Harness opportunities for advancing the uptake and use of CCA assessments, including leveraging the strengths of key partners particularly the founding Academies.Publication and Creative Services
• Oversee the creative services, quality control, and publication of all CCA’s expert panel reports including translation, layout, quality assurance, graphic design, proofreading, and printing processes.
• Oversee the creative development and publication of all CCA’s corporate materials including the Annual Report and Corporate Plan through content development, editing, layout, translation, graphic design, proofreading, and printing processes.Advice and Issues Management
• Provide strategic advice and support to the President’s Office, Board of Directors, Committees, and CCA staff about increasing the overall impact of CCA expert panel reports, brand awareness, outreach opportunities, and effective science communication.
• Provide support to the President by anticipating project-based or organizational issues, understanding potential implications, and suggesting strategic management solutions.
• Ensure consistent messages, style, and approaches in the delivery of all internal and external communications across the organization.Leadership
• Mentor, train, and advise up to five communications and publishing staff on a day-to-day basis and complete annual performance reviews and planning.
• Lead the development and implementation of all CCA-wide policy and procedures relating to all aspects of communications and publishing.
• Represent the issues, needs, and ongoing requirements for the communications and publishing staff as a member of the CCA senior management team.Knowledge Requirements
The Director of Communications requires:
• Superior knowledge of communications and public relations principles – preferably as it applies in a non-profit or academic setting;
• Extensive experience in communications planning and issues management;
• Knowledge of current research, editorial, and publication production standards and procedures including but not limited to: translation, copy-editing, layout/design, proofreading and publishing;
• Knowledge of evaluating impact of reports and assessments;
• Knowledge in developing content strategy, knowledge mobilization techniques, and creative services and design;
• Knowledge of human resource management techniques and experience managing a team;
• Experience in coordinating, organizing and implementing communications activities including those involving sensitive topics;
• Knowledge of the relationships and major players in Canada’s intramural and extramural science and public policy ecosystem, including awareness of federal science departments and Parliamentary committees, funding bodies, and related research groups;
• Knowledge of Microsoft Office Suite, Adobe Creative Suite, WordPress and other related programs;
• Knowledge of a variety of social media platforms and measurement tools.Skills Requirements
The Director of Communications must have:
• Superior time and project management skills
• Superior writing skills
• Superior ability to think strategically regarding how best to raise the CCA’s profile and ensure impact of the CCA’s expert panel reports
• Ability to be flexible and adaptable; able to respond quickly to unanticipated demands
• Strong advisory, negotiation, and problem-solving skills
• Strong skills in risk mitigation
• Superior ability to communicate in both written and oral forms, effectively and diplomatically
• Ability to mentor, train, and provide constructive feedback to direct reportsEducation and Experience
This knowledge and skillset is typically obtained through the completion of a post-secondary degree in Journalism, Communications, Public Affairs or a related field, and/or a minimum of 10
years of progressive and related experience. Experience in an organization that has addressed topics in public policy would be valuable.Language Requirements: This position is English Essential. Fluency in French is a strong asset.
To apply to this position please send your CV and cover letter to careers@scienceadvice.ca before November 5, 2018. The cover letter should answer the following questions in 1,000 words or less:
1. How does your background and work experience make you well-suited for the position of Director of Communications at CCA?
2. What trends do you see emerging in the communications field generally, and in science and policy communications more specifically? How might CCA take advantage of these trends and developments?
3. Knowing that CCA is in the business of conducting assessments of evidence on important policy topics, how do you feel communicating this type of science differs from communicating other types of information and knowledge?
Improving Innovation Through Better Management
The Council of Canadian Academies released their ‘Improving Innovation Through Better Management‘ report on October 18, 2018..As some of my regular readers (assuming there are some) might have predicted, I have issues.
There’s a distinct disconnection between the described problem and the questions to be answered. From the ‘Improving Innovation Through Better Management‘ summary webpage,
While research is world-class and technology start-ups are thriving, few companies grow and mature in Canada. This cycle — invent and sell, invent and sell — allows other countries to capture much of the economic and social benefits of Canadian-invented products, processes, marketing methods, and business models. …
So, the problem is ‘invent and sell’. Leaving aside the questionable conclusion that other countries are reaping the benefits of Canadian innovation (I’ll get back to that shortly), what questions could you ask about how to break the ‘invent and sell, invent and sell’ cycle? Hmm, maybe we should ask, How do we break the ‘invent and sell’ cycle in Canada?
The government presented two questions to deal with the problem and no, how to break the cycle is not one of the questions. From the ‘Improving Innovation Through Better Management‘ summary webpage,
… Escaping this cycle may be aided through education and training of innovation managers who can systematically manage ideas for commercial success and motivate others to reimagine innovation in Canada.
To understand how to better support innovation management in Canada, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED) asked the CCA two critical questions: What are the key skills required to manage innovation? And, what are the leading practices for teaching these skills in business schools, other academic departments, colleges/polytechnics, and industry?
As lawyers, journalists, scientists, doctors, librarians, and anyone who’s ever received misinformation can tell you, asking the right questions can make a big difference.
As for the conclusion that other countries are reaping the benefits of Canadian innovation, is there any supporting data? We enjoy a very high standard of living and have done so for at least a couple of generations. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has a Better Life Index, which ranks well-being on these 11 dimensions (from the OECD Better Life Index entry on Wikipedia), Note: Links have been removed,
- Housing: housing conditions and spendings (e.g. real estate pricing)
- Income: household income and financial wealth
- Jobs: earnings, job security and unemployment
- Community: quality of social support network
- Education: education and what you get out of it
- Environment: quality of environment (e.g. environmental health)
- Governance: involvement in democracy
- Health
- Life Satisfaction: level of happiness
- Safety: murder and assault rates
- Work-life balance
In 2017, the index ranked Canada as fifth in the world while the US appears to have slipped from a previous ranking of 7th to 8th. (See these Wikipedia entries with relevant subsections for rankings: OECD Better Life Index; Rankings, 2017 ranking and Standard of living in the United States, Measures, 3rd paragraph.)
This notion that other countries are profiting from Canadian innovation while we lag behind has been repeated so often that it’s become an article of faith and I never questioned it until someone else challenged me. This article of faith is repeated internationally and sometimes seems that every country in the world is worried that someone else will benefit from their national innovation.
Getting back to the Canadian situation, we’ve decided to approach the problem by not asking questions about our article of faith or how to break the ‘invent and sell’ cycle. Instead of questioning an assumption and producing an open-ended question, we have these questions (1) What are the key skills required to manage innovation? (2) And, what are the leading practices for teaching these skills in business schools, other academic departments, colleges/polytechnics, and industry?
in my world that first question, would be a second tier question, at best. The second question, presupposes the answer: more training in universities and colleges. I took a look at the report’s Expert Panel webpage and found it populated by five individuals who are either academics or have strong ties to academe. They did have a workshop and the list of participants does include people who run businesses, from the Improving Innovation Through Better Management‘ report (Note: Formatting has not been preserved),
Workshop Participants
Max Blouw,
Former President and Vice-Chancellor of
Wilfrid Laurier University (Waterloo, ON)Richard Boudreault, FCAE,
Chairman, Sigma Energy
Storage (Montréal, QC)Judy Fairburn, FCAE,
Past Board Chair, Alberta Innovates;
retired EVP Business Innovation & Chief Digital Officer,
Cenovus Energy Inc. (Calgary, AB)Tom Jenkins, O.C., FCAE,
Chair of the Board, OpenText
(Waterloo, ON)Sarah Kaplan,
Director of the Institute for Gender and the
Economy and Distinguished Professor, Rotman School of
Management, University of Toronto (Toronto, ON)Jean-Michel Lemieux,
Senior Vice President of Engineering,
Shopify Inc. (Ottawa, ON)Elicia Maine,
Academic Director and Professor, i2I, Beedie
School of Business, Simon Fraser University (Vancouver, BC)Kathy Malas,
Innovation Platform Manager, CHU
Sainte Justine (Montréal, QC)John L. Mann, FCAE,
Owner, Mann Consulting
(Blenheim, ON)Jesse Rodgers,
CEO, Volta Labs (Halifax, NS)Creso Sá,
Professor of Higher Education and Director of
the Centre for the Study of Canadian and International
Higher Education, Ontario Institute for Studies in Education,
University of Toronto (Toronto, ON)Dhirendra Shukla,
Professor and Chair, J. Herbert Smith
Centre for Technology Management & Entrepreneurship,
Faculty of Engineering, University of New Brunswick
(Fredericton, NB)Dan Sinai,
Senior Executive, Innovation, IBM Canada
(Toronto, ON)Valerie Walker,
Executive Director, Business/Higher
Education Roundtable (Ottawa, ON)J. Mark Weber,
Eyton Director, Conrad School of
Entrepreneurship & Business, University of Waterloo
(Waterloo, ON)
I am a little puzzled by the IBM executive’s presence (Dan Sinai) on this list. Wouldn’t Canadians holding onto their companies be counterproductive to IBM’s interests? As for John L. Mann, I’ve not been able to find him or his consulting company online. it’s unusual not to find any trace of an individual or company online these days.
In all there were nine individuals representing academic or government institutions in this list. The gender balance is 10 males and five females for the workshop participants and three males and two females for the expert panel. There is no representation from the North or from Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Prince Edward Island, or Newfoundland.
If they’re serious about looking at how to use innovation to drive higher standards of living, why aren’t there any people from Asian countries where they have been succeeding at that very project? South Korea and China come to mind.
I’m sure there are some excellent ideas in the report, I just wish they’d taken their topic to heart and actually tried to approach innovation in Canada in an innovative fashion.
Meanwhile, Vancouver gets another technology hub, from an October 30, 2018 article by Kenneth Chan for the Daily Hive (Vancouver [Canada]), Note: Links have been removed,
Vancouver’s rapidly growing virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tech sectors will greatly benefit from a new VR and AR hub created by Launch Academy.
The technology incubator has opened a VR and AR hub at its existing office at 300-128 West Hastings Street in downtown, in partnership with VR/AR Association Vancouver. Immersive tech companies have access to desk space, mentorship programs, VR/AR equipment rentals, investor relations connected to Silicon Valley [emphasis mine], advisory services, and community events and workshops.
…
Within the Vancouver tech industry, the immersive sector has grown from 15 companies working in VR and AR in 2015 to 220 organizations today.
…
Globally, the VR and AR market is expected to hit a value of $108 billion by 2021, with tech giants like Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google, and Microsoft [emphasis mine] investing billions into product development.
…
In the Vancouver region, the ‘invent and sell’ cycle can be traced back to the 19th century.
One more thing, as I was writing this piece I tripped across this news: “$7.7-billion pact makes Encana more American than Canadian‘ by Geoffrey Morgan. It’s in the Nov. 2, 2018 print edition of the Vancouver Sun’s front page for business. “Encana Corp., the storied Canadian company that had been slowly transitioning away from Canada and natural gas over the past few years under CEO [Chief Executive Officer] Doug Suttles, has pivoted aggressively to US shale basins. … Suttles, formerly as BP Plc. executive, moved from Calgary [Alberta, Canada] to Denver [Colorado, US], though the company said that was for personal reasons and not a precursor to relocation of Encana’s headquarters.” Yes, that’s quite believable. By the way, Suttles has spent* most of his life in the US (Wikipedia entry).
In any event, it’s not just Canadian emerging technology companies that get sold or somehow shifted out of Canada.
So, should we break the cycle and, if so, how are we going to do it?
*’spend’ corrected to ‘spent’ on November 6, 2018.
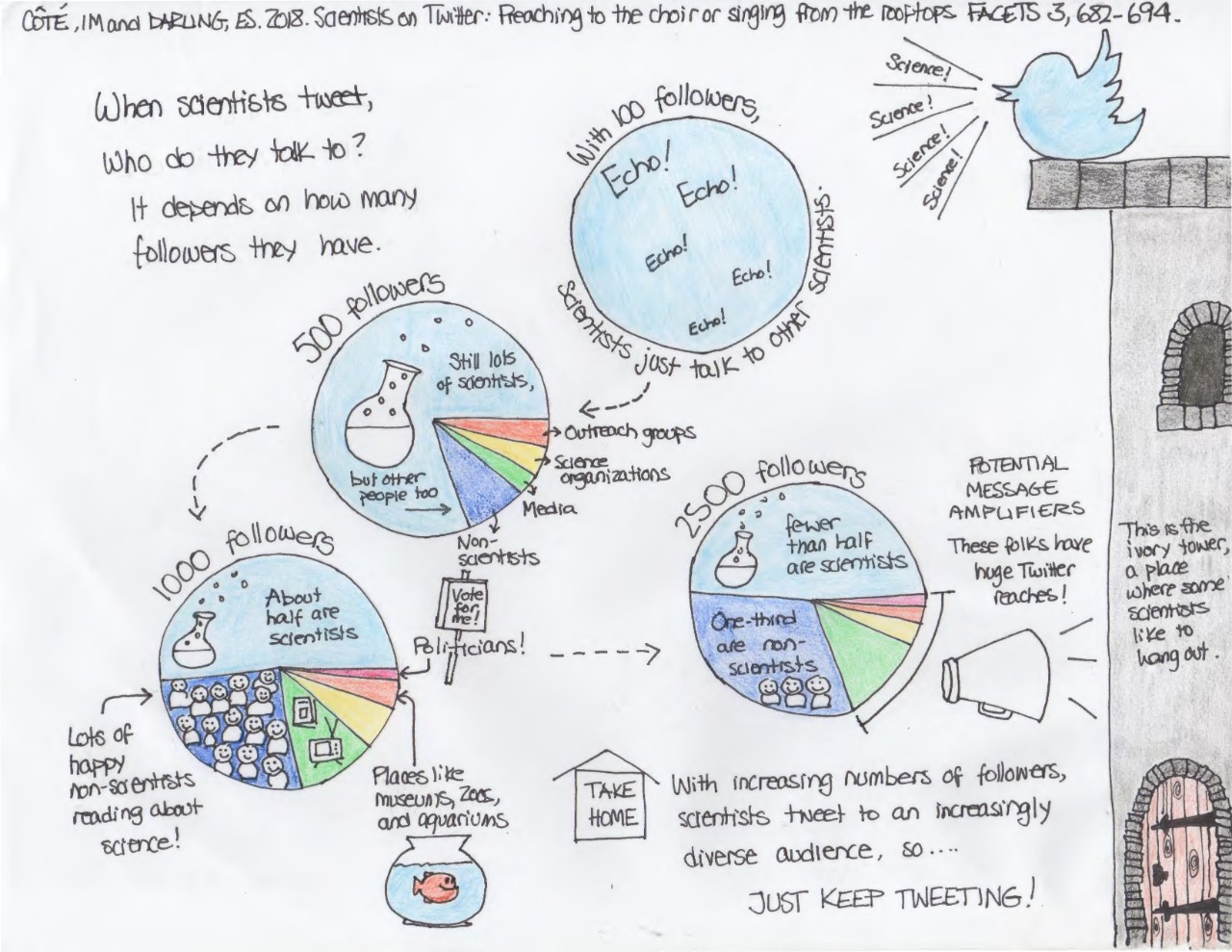
 Fig. 1. Conceptual depiction of inreach and outreach for Twitter communication by academic faculty. Left: If Twitter functions as an inreach tool, tweeting scientists might primarily reach only other scientists and perhaps, over time (arrow), some applied conservation and management science organizations. Right: If Twitter functions as an outreach tool, tweeting scientists might first reach other scientists, but over time (arrow) they will eventually attract members of the media, members of the public who are not scientists, and decision-makers (not necessarily in that order) as followers.
Fig. 1. Conceptual depiction of inreach and outreach for Twitter communication by academic faculty. Left: If Twitter functions as an inreach tool, tweeting scientists might primarily reach only other scientists and perhaps, over time (arrow), some applied conservation and management science organizations. Right: If Twitter functions as an outreach tool, tweeting scientists might first reach other scientists, but over time (arrow) they will eventually attract members of the media, members of the public who are not scientists, and decision-makers (not necessarily in that order) as followers.




















