At long last, the end is in sight! This last part is mostly a collection of items that don’t fit elsewhere or could have fit elsewhere but that particular part was already overstuffed.
Podcasting science for the people
March 2009 was the birth date for a podcast, then called Skeptically Speaking and now known as Science for the People (Wikipedia entry). Here’s more from the Science for the People About webpage,
Science for the People is a long-format interview podcast that explores the connections between science, popular culture, history, and public policy, to help listeners understand the evidence and arguments behind what’s in the news and on the shelves.
Every week, our hosts sit down with science researchers, writers, authors, journalists, and experts to discuss science from the past, the science that affects our lives today, and how science might change our future.
THE TEAM
Rachelle Saunders: Producer & Host
I love to learn new things, and say the word “fascinating” way too much. I like to talk about intersections and how science and critical thinking intersect with everyday life, politics, history, and culture. By day I’m a web developer, and I definitely listen to way too many podcasts.
….
H/t to GeekWrapped’s 20 Best Science Podcasts.
Science: human contexts and cosmopolitanism
situating science: Science in Human Contexts was a seven-year project ending in 2014 and funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC). Here’s more from their Project Summary webpage,
Created in 2007 with the generous funding of the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada Strategic Knowledge Cluster grant, Situating Science is a seven-year project promoting communication and collaboration among humanists and social scientists that are engaged in the study of science and technology.
…
You can find out more about Situating Science’s final days in my August 16, 2013 posting where I included a lot of information about one of their last events titled, “Science and Society 2013 Symposium; Emerging Agendas for Citizens and the Sciences.”
…
The “think-tank” will dovetail nicely with a special symposium in Ottawa on Science and Society Oct. 21-23. For this symposium, the Cluster is partnering with the Institute for Science, Society and Policy to bring together scholars from various disciplines, public servants and policy workers to discuss key issues at the intersection of science and society. [emphasis mine] The discussions will be compiled in a document to be shared with stakeholders and the wider public.
The team will continue to seek support and partnerships for projects within the scope of its objectives. Among our top priorities are a partnership to explore sciences, technologies and their publics as well as new partnerships to build upon exchanges between scholars and institutions in India, Singapore and Canada.
…
The Situating Science folks did attempt to carry on the organization’s work by rebranding the organization to call it the Canadian Consortium for Situating Science and Technology (CCSST). It seems to have been a short-lived volunteer effort.
Meanwhile, the special symposium held in October 2013 appears to have been the springboard for another SSHRC funded multi-year initiative, this time focused on science collaborations between Canada, India, and Singapore, Cosmopolitanism and the Local in Science and Nature from 2014 – 2017. Despite their sunset year having been in 2017, their homepage boasts news about a 2020 Congress and their Twitter feed is still active. Harking back, here’s what the project was designed to do, from the About Us page,
Welcome to our three year project that will establish a research network on “Cosmopolitanism” in science. It closely examines the actual types of negotiations that go into the making of science and its culture within an increasingly globalized landscape. This partnership is both about “cosmopolitanism and the local” and is, at the same time, cosmopolitan and local.
Anyone who reads this blog with any frequency will know that I often comment on the fact that when organizations such as the Council of Canadian Academies bring in experts from other parts of the world, they are almost always from the US or Europe. So, I was delighted to discover the Cosmopolitanism project and featured it in a February 19, 2015 posting.
Here’s more from Cosmopolitanism’s About Us page
Specifically, the project will:
- Expose a hitherto largely Eurocentric scholarly community in Canada to widening international perspectives and methods,
- Build on past successes at border-crossings and exchanges between the participants,
- Facilitate a much needed nation-wide organization and exchange amongst Indian and South East Asian scholars, in concert with their Canadian counterparts, by integrating into an international network,
- Open up new perspectives on the genesis and place of globalized science, and thereby
- Offer alternative ways to conceptualize and engage globalization itself, and especially the globalization of knowledge and science.
- Bring the managerial team together for joint discussion, research exchange, leveraging and planning – all in the aid of laying the grounds of a sustainable partnership
Eco Art (also known as ecological art or environmental art)
I’m of two minds as to whether I should have tried to stuff this into the art/sci subsection in part 2. On balance, I decided that this merited its own section and that part 2 was already overstuffed.
Let’s start in Newfoundland and Labrador with Marlene Creates (pronounced Kreets), here’s more about her from her website’s bio webpage,
Marlene Creates (pronounced “Kreets”) is an environmental artist and poet who works with photography, video, scientific and vernacular knowledge, walking and collaborative site-specific performance in the six-acre patch of boreal forest in Portugal Cove, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, where she lives.
…
For almost 40 years her work has been an exploration of the relationship between human experience, memory, language and the land, and the impact they have on each other. …
…
Currently her work is focused on the six acres of boreal forest where she lives in a ‘relational aesthetic’ to the land. This oeuvre includes Water Flowing to the Sea Captured at the Speed of Light, Blast Hole Pond River, Newfoundland 2002–2003, and several ongoing projects:
…
Marlene Creates received a Governor General’s Award in Visual and Media Arts for “Lifetime Artistic Achievement” in 2019. …
As mentioned in her bio, Creates has a ‘forest’ project. The Boreal Poetry Garden,
Portugal Cove, Newfoundland 2005– (ongoing) . If you are interested in exploring it, she has created a virtual walk here. Just click on one of the index items on the right side of the screen to activate a video.
An October 1, 2018 article by Yasmin Nurming-Por for Canadian Art magazine features 10 artists who focus on environmental and/or land art themes,
As part of her 2016 master’s thesis exhibition, Fredericton [New Brunswick] artist Gillian Dykeman presented the video Dispatches from the Feminist Utopian Future within a larger installation that imagined various canonical earthworks from the perspective of the future. It’s a project that addresses the inherent sense of timelessness in these massive interventions on the natural landscape from the perspective of contemporary land politics. … she proposes a kind of interaction with the invasive and often colonial gestures of modernist Land art, one that imagines a different future for these earthworks, where they are treated as alien in a landscape and as beacons from a feminist future.
…
A video trailer featuring “DISPATCHES FROM THE FEMINIST UTOPIAN FUTURE” (from Dykeman’s website archive page featuring the show,
If you have the time, I recommend reading the article in its entirety.
Oddly, I did not expect Vancouver to have such an active eco arts focus. The City of Vancouver Parks Board maintains an Environmental Art webpage on its site listing a number of current and past projects.
I cannot find the date for when this Parks Board initiative started but I did find a document produced prior to a Spring 2006 Arts & Ecology think tank held in Vancouver under the auspices of the Canada Council for the Arts, the Canadian Commission for UNESCO, the Vancouver Foundation, and the Royal Society for the Encouragement of the Arts, Manufactures and Commerce (London UK).
In all likelihood, Vancouver Park Board’s Environmental Art webpage was produced after 2006.
I imagine the document and the think tank session helped to anchor any then current eco art projects and encouraged more projects.
The document (MAPPING THE TERRAIN OF CONTEMPORARY ECOART PRACTICE AND COLLABORATION) while almost 14 years old offers a fascinating overview of what was happening internationally and in Canada.
While its early days were in 2008, EartHand Gleaners (Vancouver-based) wasn’t formally founded as an arts non-for-profit organization until 2013. You can find out more about them and their projects here.
Eco Art has been around for decades according to the eco art think tank document but it does seemed to have gained momentum here in Canada over the last decade.
Photography and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)
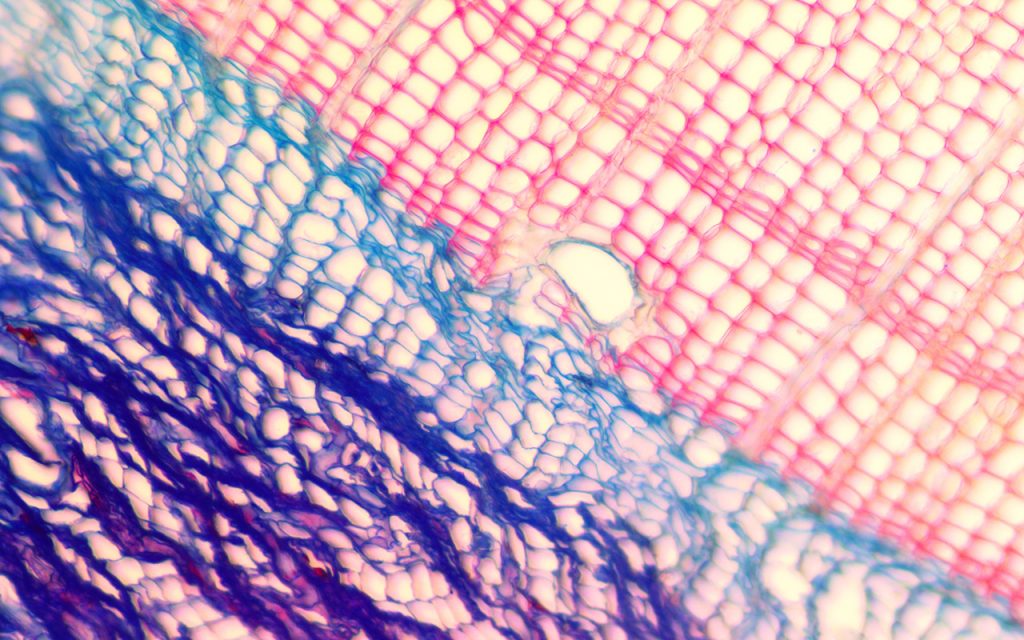
Exploring the jack pine tight knit family tree. Credit: Dana Harris Brock University (2018)
Pictured are developing phloem, cambial, and xylem cells (blue), and mature xylem cells (red), in the outermost portion of a jack pine tree. This research aims to identify the influences of climate on the cellular development of the species at its northern limit in Yellowknife, NT. The differences in these cell formations is what creates the annual tree ring boundary.
Science Exposed is a photography contest for scientists which has been run since 2016 (assuming the Past Winners archive is a good indicator for the programme’s starting year).
The 2020 competition recently closed but public voting should start soon. It’s nice to see that NSERC is now making efforts to engage members of the general public rather than focusing its efforts solely on children. The UK’s ASPIRES project seems to support the idea that adults need to be more fully engaged with STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) efforts as it found that children’s attitudes toward science are strongly influenced by their parents’ and relatives’ attitudes.(See my January 31, 2012 posting.)
Ingenious, the book and Ingenium, the science museums
To celebrate Canada’s 150th anniversary in 2017, then Governor General David Johnston and Tom Jenkins (Chair of the board for Open Text and former Chair of the federal committee overseeing the ‘Review of Federal Support to R&’D [see my October 21, 2011 posting about the resulting report]) wrote a boo about Canada’s inventors and inventions.
Johnston and Jenkins jaunted around the country launching their book (I have more about their June 1, 2017 Vancouver visit in a May 30, 2017 posting; scroll down about 60% of the way]).
The book’s full title, “Ingenious: How Canadian Innovators Made the World Smarter, Smaller, Kinder, Safer, Healthier, Wealthier and Happier ” outlines their thesis neatly.
Not all that long after the book was launched, there was a name change (thankfully) for the Canada Science and Technology Museums Corporation (CSTMC). It is now known as Ingenium (covered in my August 10, 2017 posting).
The reason that name change was such a relief (for those who don’t know) is that the corporation included three national science museums: Canada Aviation and Space Museum, Canada Agriculture and Food Museum, and (wait for it) Canada Science and Technology Museum. On the list of confusing names, this ranks very high for me. Again, I give thanks for the change from CSTMC to Ingenium, leaving the name for the museum alone.
2017 was also the year that the newly refurbished Canada Science and Technology Museum was reopened after more than three years (see my June 23, 2017 posting about the November 2017 reopening and my June 12, 2015 posting for more information about the situation that led to the closure).
A Saskatchewan lab, Convergence, Order of Canada, Year of Science, Animated Mathematics, a graphic novel, and new media
Since this section is jampacked, I’m using subheads.
Saskatchewan
Dr. Brian Eames hosts an artist-in-residence, Jean-Sebastien (JS) Gauthier at the University of Saskatchewan’s College of Medicine Eames Lab. A February 16, 2018 posting here featured their first collaboration together. It covered evolutionary biology, the synchrotron (Canadian Light Source [CLS]) in Saskatoon, and the ‘ins and outs’ of a collaboration between a scientist an artist. Presumably the art-in-residence position indicates that first collaboration went very well.
In January 2020, Brian kindly gave me an update on their current projects. Jean-Sebastin successfully coded an interactive piece for an exhibit at the 2019 Nuit Blanche Saskatoon event using Connect (Xbox). More recently, he got a VR [virtual reality] helmet for an upcoming project or two.
After much clicking on the Nuit Blanche Saskatoon 2019 interactive map, I found this,
Our Glass is a work of interactive SciArt co-created by artist JS Gauthier and biologist Dr Brian F. Eames. It uses cutting-edge 3D microscopic images produced for artistic purposes at the Canadian Light Source, Canada’s only synchrotron facility. Our Glass engages viewers of all ages to peer within an hourglass showing how embryonic development compares among animals with whom we share a close genetic heritage.
Eames also mentioned they were hoping to hold an international SciArt Symposium at the University of Saskatchewan in 2021.
Convergence
Dr. Cristian Zaelzer-Perez, an instructor at Concordia University (Montreal; read this November 20, 2019 Concordia news release by Kelsey Rolfe for more about his work and awards), in 2016 founded the Convergence Initiative, a not-for-profit organization that encourages interdisciplinary neuroscience and art collaborations.
Cat Lau’s December 23, 2019 posting for the Science Borealis blog provides insight into Zaelzer-Perez’s relationship to science and art,
…
Cristian: I have had a relationship with art and science ever since I have had memory. As a child, I loved to do classifications, from grouping different flowers to collecting leaves by their shapes. At the same time, I really loved to draw them and for me, both things never looked different; they (art and science) have always worked together.
I started as a graphic designer, but the pursuit to learn about nature was never dead. At some point, I knew I wanted to go back to school to do research, to explore and learn new things. I started studying medical technologies, then molecular biology and then jumped into a PhD. At that point, my life as a graphic designer slipped down, because of the focus you have to give to the discipline. It seemed like every time I tried to dedicate myself to one thing, I would find myself doing the other thing a couple years later.
I came to Montreal to do my post-doc, but I had trouble publishing, which became problematic in getting a career. I was still loving what I was doing, but not seeing a future in that. Once again, art came back into my life and at the same time I saw that science was becoming really hard to understand and scientists were not doing much to bridge the gap.
…
The Convergence Initiative has an impressive array of programmes. Do check it out.
Order of Canada and ‘The Science Lady’
For a writer of children’s science books, an appointment to the Order of Canada is a singular honour. I cannot recall a children’s science book writer previous to Shar Levine being appointed as a Member of the Order of Canada. Known as ‘The Science Lady‘, Levine was appointed in 2016. Here’s more from her Wikipedia entry, Note: Links have been removed,
Shar Levine (born 1953) is an award-winning, best selling Canadian children’s author, and designer.
Shar has written over 70 books and book/kits, primarily on hands-on science for children. For her work in Science literacy and Science promotion, Shar has been appointed to the 2016 Order of Canada. In 2015, she was recognized by the University of Alberta and received their Alumni Honour Award. Levine, and her co-author, Leslie Johnstone, were co-recipients of the Eve Savory Award for Science Communication from the BC Innovation Council (2006) and their book, Backyard Science, was a finalist for the Subaru Award, (hands on activity) from the American Association for the Advancement of Science, Science Books and Films (2005). The Ultimate Guide to Your Microscope was a finalist-2008 American Association for the Advancement of Science/Subaru Science Books and Films Prize Hands -On Science/Activity Books.
…
To get a sense of what an appointment to the Order of Canada means, here’s a description from the government of Canada website,
The Order of Canada is how our country honours people who make extraordinary contributions to the nation.
Since its creation in 1967—Canada’s centennial year—more than 7 000 people from all sectors of society have been invested into the Order. The contributions of these trailblazers are varied, yet they have all enriched the lives of others and made a difference to this country. Their grit and passion inspire us, teach us and show us the way forward. They exemplify the Order’s motto: DESIDERANTES MELIOREM PATRIAM (“They desire a better country”).
…
Year of Science in British Columbia
In the Fall of 2010, the British Columbia provincial government announced a Year of Science (coinciding with the school year) . Originally, it was supposed to be a provincial government-wide initiative but the idea percolated through any number of processes and emerged as a year dedicated to science education for youth (according to the idea’s originator, Moira Stilwell who was then a Member of the Legislative Assembly [MLA]’ I spoke with her sometime in 2010 or 2011).
As the ‘year’ drew to a close, there was a finale ($1.1M in funding), which was featured here in a July 6, 2011 posting.
The larger portion of the money ($1M) was awarded to Science World while $100,000 ($0.1 M) was given to the Pacific Institute of Mathematical Sciences To my knowledge there have been no followup announcements about how the money was used.
Animation and mathematics
In Toronto, mathematician Dr. Karan Singh enjoyed a flurry of interest due to his association with animator Chris Landreth and their Academy Award (Oscar) Winning 2004 animated film, Ryan. They have continued to work together as members of the Dynamic Graphics Project (DGP) Lab at the University of Toronto. Theirs is not the only Oscar winning work to emerge from one or more of the members of the lab. Jos Stam, DGP graduate and adjunct professor won his third in 2019.
A graphic novel and medical promise
An academic at Simon Fraser University since 2015, Coleman Nye worked with three other women to produce a graphic novel about medical dilemmas in a genre described as’ ethno-fiction’.
Lissa: A Story about Medical Promise, Friendship, and Revolution (2017) by Sherine Hamdy and Coleman Nye, two anthropologists and Art by Sarula Bao and Caroline Brewer, two artists.
Here’s a description of the book from the University of Toronto Press website,
As young girls in Cairo, Anna and Layla strike up an unlikely friendship that crosses class, cultural, and religious divides. Years later, Anna learns that she may carry the hereditary cancer gene responsible for her mother’s death. Meanwhile, Layla’s family is faced with a difficult decision about kidney transplantation. Their friendship is put to the test when these medical crises reveal stark differences in their perspectives…until revolutionary unrest in Egypt changes their lives forever.
The first book in a new series [ethnoGRAPIC; a series of graphic novels from the University of Toronto Press], Lissa brings anthropological research to life in comic form, combining scholarly insights and accessible, visually-rich storytelling to foster greater understanding of global politics, inequalities, and solidarity.
I hope to write more about this graphic novel in a future posting.
New Media
I don’t know if this could be described as a movement yet but it’s certainly an interesting minor development. Two new media centres have hosted, in the last four years, art/sci projects and/or workshops. It’s unexpected given this definition from the Wikipedia entry for New Media (Note: Links have been removed),
New media are forms of media that are computational and rely on computers for redistribution. Some examples of new media are computer animations, computer games, human-computer interfaces, interactive computer installations, websites, and virtual worlds.[1][2]
In Manitoba, the Video Pool Media Arts Centre hosted a February 2016 workshop Biology as a New Art Medium: Workshop with Marta De Menezes. De Menezes, an artist from Portugal, gave workshops and talks in both Winnipeg (Manitoba) and Toronto (Ontario). Here’s a description for the one in Winnipeg,
This workshop aims to explore the multiple possibilities of artistic approaches that can be developed in relation to Art and Microbiology in a DIY situation. A special emphasis will be placed on the development of collaborative art and microbiology projects where the artist has to learn some biological research skills in order to create the artwork. The course will consist of a series of intense experimental sessions that will give raise to discussions on the artistic, aesthetic and ethical issues raised by the art and the science involved. Handling these materials and organisms will provoke a reflection on the theoretical issues involved and the course will provide background information on the current diversity of artistic discourses centred on biological sciences, as well a forum for debate.
…
VIVO Media Arts Centre in Vancouver hosted the Invasive Systems in 2019. From the exhibition page,
Picture this – a world where AI invades human creativity, bacteria invade our brains, and invisible technological signals penetrate all natural environments. Where invasive species from plants to humans transform spaces where they don’t belong, technology infiltrates every aspect of our daily lives, and the waste of human inventions ravages our natural environments.
…
This weekend festival includes an art-science exhibition [emphasis mine], a hands-on workshop (Sat, separate registration required), and guided discussions and tours by the curator (Sat/Sun). It will showcase collaborative works by three artist/scientist pairs, and independent works by six artists. Opening reception will be on Friday, November 8 starting at 7pm; curator’s remarks and performance by Edzi’u at 7:30pm and 9pm.
New Westminster’s (British Columbia) New Media Gallery recently hosted an exhibition, ‘winds‘ from June 20 – September 29, 2019 that could be described as an art/sci exhibition,
Landscape and weather have long shared an intimate connection with the arts. Each of the works here is a landscape: captured, interpreted and presented through a range of technologies. The four artists in this exhibition have taken, as their material process, the movement of wind through physical space & time. They explore how our perception and understanding of landscape can be interpreted through technology.
These works have been created by what might be understood as a sort of scientific method or process that involves collecting data, acute observation, controlled experiments and the incorporation of measurements and technologies that control or collect motion, pressure, sound, pattern and the like. …
Council of Canadian Academies, Publishing, and Open Access
Established in 2005, the Council of Canadian Academies (CCA) (Wikipedia entry) is tasked by various departments and agencies to answer their queries about science issues that could affect the populace and/or the government. In 2014, the CCA published a report titled, Science Culture: Where Canada Stands. It was in response to the Canada Science and Technology Museums Corporation (now called Ingenium), Industry Canada, and Natural Resources Canada and their joint request that the CCA conduct an in-depth, independent assessment to investigate the state of Canada’s science culture.
I gave a pretty extensive analysis of the report, which I delivered in four parts: Part 1, Part 2 (a), Part 2 (b), and Part 3. In brief, the term ‘science culture’ seems to be specifically, i.e., it’s not used elsewhere in the world (that we know of), Canadian. We have lots to be proud of. I was a little disappointed by the lack of culture (arts) producers on the expert panel and, as usual, I bemoaned the fact that the international community included as reviewers, members of the panel, and as points for comparison were drawn from the usual suspects (US, UK, or somewhere in northern Europe).
Science publishing in Canada took a bit of a turn in 2010, when the country’s largest science publisher, NRC (National Research Council) Research Publisher was cut loose from the government and spun out into the private, *not-for-profit publisher*, Canadian Science Publishing (CSP). From the CSP Wikipedia entry,
Since 2010, Canadian Science Publishing has acquired five new journals:
- Canadian Journal of Animal Science
- Canadian Journal of Plant Science
- Canadian Journal of Soil Science
- Geomatica
- Transactions of the Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering
Since 2010, Canadian Science Publishing has also launched four new journals
Canadian Science Publishing offers researchers options to make their published papers freely available (open access) in their standard journals and in their open access journal, (from the CSP Wikipedia entry)
Arctic Science aims to provide a collaborative approach to Arctic research for a diverse group of users including government, policy makers, the general public, and researchers across all scientific fields
FACETS is Canada’s first open access multidisciplinary science journal, aiming to advance science by publishing research that the multi-faceted global community of research. FACETS is the official journal of the Royal Society of Canada’s Academy of Science.
Anthropocene Coasts aims to understand and predict the effects of human activity, including climate change, on coastal regions.
In addition, Canadian Science Publishing strives to make their content accessible through the CSP blog that includes plain language summaries of featured research. The open-access journal FACETS similarly publishes plain language summaries.
*comment removed*
CSP announced (on Twitter) a new annual contest in 2016,
Canadian Science Publishing@cdnsciencepub
New CONTEST! Announcing Visualizing Science! Share your science images & win great prizes! Full details on the blog http://cdnsciencepub.com/blog/2016-csp-image-contest-visualizing-science.aspx1:45 PM · Sep 19, 2016·TweetDeck
The 2016 blog posting is no longer accessible. Oddly for a contest of this type, I can’t find an image archive for previous contests. Regardless, a 2020 competition has been announced for Summer 2020. There are some details on the VISUALIZING SCIENCE 2020 webpage but some are missing, e.g., no opening date, no deadline. They are encouraging you to sign up for notices.
Back to open access, in a January 22, 2016 posting I featured news about Montreal Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute [MNI] in Québec, Canada) and its then new policy giving researchers world wide access to its research and made a pledge that it would not seek patents for its work.
Fish, Newfoundland & Labrador, and Prince Edward Island
AquAdvantage’s genetically modified salmon was approved for consumption in Canada according to my May 20, 2016 posting. The salmon are produced/farmed by a US company (AquaBounty) but the the work of genetically modifying Atlantic salmon with genetic material from the Chinook (a Pacific ocean salmon) was mostly undertaken at Memorial University in Newfoundland & Labrador.
The process by which work done in Newfoundland & Labrador becomes the property of a US company is one that’s well known here in Canada. The preliminary work and technology is developed here and then purchased by a US company, which files patents, markets, and profits from it. Interestingly, the fish farms for the AquAdvantage salmon are mostly (two out of three) located on Prince Edward Island.
Intriguingly, 4.5 tonnes of the modified fish were sold for consumption in Canada without consumers being informed (see my Sept. 13, 2017 posting, scroll down about 45% of the way).
It’s not all sunshine and roses where science culture in Canada is concerned. Incidents where Canadians are not informed let alone consulted about major changes in the food supply and other areas are not unusual. Too many times, scientists, politicians, and government policy experts want to spread news about science without any response from the recipients who are in effect viewed as a ‘tabula rasa’ or a blank page.
Tying it all up
This series has been my best attempt to document in some fashion or another the extraordinary range of science culture in Canada from roughly 2010-19. Thank you! This series represents a huge amount of work and effort to develop science culture in Canada and I am deeply thankful that people give so much to this effort.
I have inevitably missed people and organizations and events. For that I am very sorry. (There is an addendum to the series as it’s been hard to stop but I don’t expect to add anything or anyone more.)
I want to mention but can’t expand upon,the Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy, which was established in the 2017 federal budget (see a March 31, 2017 posting about the Vector Institute and Canada’s artificial intelligence sector).
Science Borealis, the Canadian science blog aggregator, owes its existence to Canadian Science Publishing for the support (programming and financial) needed to establish itself and, I believe, that support is still ongoing. I think thanks are also due to Jenny Ryan who was working for CSP and championed the initiative. Jenny now works for Canadian Blood Services. Interestingly, that agency added a new programme, a ‘Lay Science Writing Competition’ in 2018. It’s offered n partnership with two other groups, the Centre for Blood Research at the University of British Columbia and Science Borealis
While the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada does not fit into my time frame as it lists as its founding date December 1, 1868 (18 months after confederation), the organization did celebrate its 150th anniversary in 2018.
Vancouver’s Electric Company often produces theatrical experiences that cover science topics such as the one featured in my June 7, 2013 posting, You are very star—an immersive transmedia experience.
Let’s Talk Science (Wikipedia entry) has been heavily involved with offering STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) programming both as part of curricular and extra-curricular across Canada since 1993.
This organization predates confederation having been founded in 1849 by Sir Sandford Fleming and Kivas Tully in Toronto. for surveyors, civil engineers, and architects. It is the Royal Canadian Institute of Science (Wikipedia entry)_. With almost no interruption, they have been delivering a regular series of lectures on the University of Toronto campus since 1913.
The Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics is a more recent beast. In 1999 Mike Lazirides, founder of Research In Motion (now known as Blackberry Limited), acted as both founder and major benefactor for this institute in Waterloo, Ontario. They offer a substantive and imaginative outreach programmes such as Arts and Culture: “Event Horizons is a series of unique and extraordinary events that aim to stimulate and enthral. It is a showcase of innovative work of the highest international standard, an emotional, intellectual, and creative experience. And perhaps most importantly, it is a social space, where ideas collide and curious minds meet.”
While gene-editing hasn’t seemed to be top-of-mind for anyone other than those in the art/sci community that may change. My April 26, 2019 posting focused on what appears to be a campaign to reverse Canada’s criminal ban on human gene-editing of inheritable cells (germline). With less potential for controversy, there is a discussion about somatic gene therapies and engineered cell therapies. A report from the Council of Canadian is due in the Fall of 2020. (The therapies being discussed do not involve germline editing.)
French language science media and podcasting
Agence Science-Presse is unique as it is the only press agency in Canada devoted to science news. Founded in 1978, it has been active in print, radio, television, online blogs, and podcasts (Baladodiffusion). You can find their Twitter feed here.
I recently stumbled across ‘un balados’ (podcast), titled, 20%. Started in January 2019 by the magazine, Québec Science, the podcast is devoted to women in science and technology. 20%, the podcast’s name, is the statistic representing the number of women in those fields. “Dans les domaines de la science et de la technologie, les femmes ne forment que 20% de la main-d’oeuvre.” (from the podcast webpage) The podcast is a co-production between “Québec Science [founded in 1962] et l’Acfas [formerly, l’Association Canadienne-Française pour l’Avancement des Sciences, now, Association francophone pour le savoir], en collaboration avec la Commission canadienne pour l’UNESCO, L’Oréal Canada et la radio Choq.ca.” (also from the podcast webpage)
Does it mean anything?
There have been many developments since I started writing this series in late December 2019. In January 2020, Iran shot down one of its own planes. That error killed some 176 people , many of them (136 Canadians and students) bound for Canada. The number of people who were involved in the sciences, technology, and medicine was striking.
It was a shocking loss and will reverberate for quite some time. There is a memorial posting here (January 13, 2020), which includes links to another memorial posting and an essay.
As I write this we are dealing with a pandemic, COVID-19, which has us all practicing physical and social distancing. Congregations of large numbers are expressly forbidden. All of this is being done in a bid to lessen the passage of the virus, SARS-CoV-2 which causes COVID-19.
In the short term at least, it seems that much of what I’ve described in these five parts (and the addendum) will undergo significant changes or simply fade away.
As for the long term, with this last 10 years having hosted the most lively science culture scene I can ever recall, I’m hopeful that science culture in Canada will do more than survive but thrive.
For anyone who missed them:
Part 1 covers science communication, science media (mainstream and others such as blogging) and arts as exemplified by music and dance: The decade that was (2010-19) and the decade to come (2020-29): Science culture in Canada (1 of 5).
Part 2 covers art/science (or art/sci or sciart) efforts, science festivals both national and local, international art and technology conferences held in Canada, and various bar/pub/café events: The decade that was (2010-19) and the decade to come (2020-29): Science culture in Canada (2 of 5).
Part 3 covers comedy, do-it-yourself (DIY) biology, chief science advisor, science policy, mathematicians, and more: The decade that was (2010-19) and the decade to come (2020-29): Science culture in Canada (3 of 5)
Part 4 covers citizen science, birds, climate change, indigenous knowledge (science), and the IISD Experimental Lakes Area: The decade that was (2010-19) and the decade to come (2020-29): Science culture in Canada (4 of 5)
*”for-profit publisher, Canadian Science Publishing (CSP)” corrected to “not-for-profit publisher, Canadian Science Publishing (CSP)” and this comment “Not bad for a for-profit business, eh?” removed on April 29, 2020 as per Twitter comments,
Canadian Science Publishing @cdnsciencepub
Hi Maryse, thank you for alerting us to your blog. To clarify, Canadian Science Publishing is a not-for-profit publisher. Thank you as well for sharing our image contest. We’ve updated the contest page to indicate that the contest opens July 2020!





