Andrew Paul’s December 4, 2023 article for Popular Science attempts to give readers a sense of the scale and this is one of those times when words are better than pictures, Note: Links have been removed,
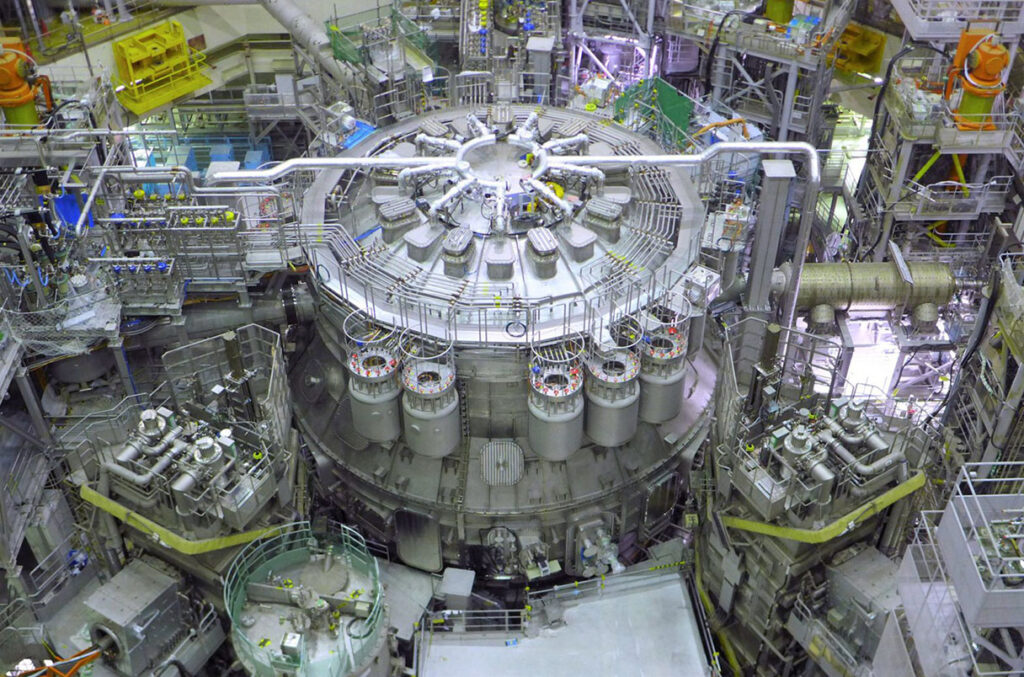
Japan and the European Union have officially inaugurated testing at the world’s largest experimental nuclear fusion plant. Located roughly 85 miles north of Tokyo, the six-story, JT-60SA “tokamak” facility heats plasma to 200 million degrees Celsius (around 360 million Fahrenheit) within its circular, magnetically insulated reactor. Although JT-60SA first powered up during a test run back in October [2023], the partner governments’ December 1 announcement marks the official start of operations at the world’s biggest fusion center, reaffirming a “long-standing cooperation in the field of fusion energy.”
The tokamak—an acronym of the Russian-language designation of “toroidal chamber with magnetic coils”—has led researchers’ push towards achieving the “Holy Grail” of sustainable green energy production for decades. …
Speaking at the inauguration event, EU energy commissioner Kadri Simson referred to the JT-60SA as “the most advanced tokamak in the world,” representing “a milestone for fusion history.”
…
But even if such a revolutionary milestone is crossed, it likely won’t be at JT-60SA. Along with its still-in-construction sibling, the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) in Europe, the projects are intended solely to demonstrate scalable fusion’s feasibility. Current hopes estimate ITER’s operational start for sometime in 2025, although the undertaking has been fraught with financial, logistical, and construction issues since its groundbreaking back in 2011.
…
See what I mean about a picture not really conveying the scale,
Dennis Normile’s October 31, 2023 article for Science magazine describes the facility’s (Japan’s JT-60SA fusion reactor) test run and future implications for the EU’s ITER project,
The long trek toward practical fusion energy passed a milestone last week when the world’s newest and largest fusion reactor fired up. Japan’s JT-60SA uses magnetic fields from superconducting coils to contain a blazingly hot cloud of ionized gas, or plasma, within a doughnut-shaped vacuum vessel, in hope of coaxing hydrogen nuclei to fuse and release energy. The four-story-high machine is designed to hold a plasma heated to 200 million degrees Celsius for about 100 seconds, far longer than previous large tokamaks.
Last week’s achievement “proves to the world that the machine fulfills its basic function,” says Sam Davis, a project manager at Fusion for Energy, an EU organization working with Japan’s National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) on JT-60SA and related programs. It will take another 2 years before JT-60SA produces the long-lasting plasmas needed for meaningful physics experiments, says Hiroshi Shirai, leader of the project for QST.
JT-60SA will also help ITER, the mammoth international fusion reactor under construction in France that’s intended to demonstrate how fusion can generate more energy than goes into producing it. ITER will rely on technologies and operating know-how that JT-60SA will test.
Japan got to host JT-60SA and two other small fusion research facilities as a consolation prize for agreeing to let ITER go to France. …
As Normile notes, the ITER project has had a long and rocky road so far.
The Canadians
As it turns out, there’s a company in British Columbia, Canada that is also on the road to fusion energy. Not so imaginatively, it’s called General Fusion but it has a different approach to developing this ‘clean energy’. (See my October 28, 2022 posting, “Overview of fusion energy scene,” which includes information about the international scene and some of the approaches, including General Fusion’s, to developing the technology and my October 11, 2023 posting offers an update to the General Fusion situation.) Since my October 2023 posting, there have been a few developments at General Fusion.
This December 4, 2023 General Fusion news release celebrates a new infusion of cash from the Canadian government and take special note of the first item in the ‘Quick Facts’ of the advantage this technology offers,
Today [December 4, 2023], General Fusion announced that Canada’s Strategic Innovation Fund (SIF) has awarded CA$5 million to support research and development to advance the company’s Magnetized Target Fusion (MTF) demonstration at its Richmond headquarters. Called LM26, this ground-breaking machine will progress major technical milestones required to commercialize zero-carbon fusion power by the early to mid-2030s. The funds are an addition to the existing contribution agreement with SIF, to support the development of General Fusion’s transformational technology.
Fusion energy is the ultimate clean energy solution. It is what powers the sun and stars. It’s the process by which two light nuclei merge to form a heavier one, emitting a massive amount of energy. By 2100, the production and export of the Canadian industry’s fusion energy technology could provide up to $1.26 trillion in economic benefits to Canada. Additionally, fusion could completely offset 600 MT CO2-e emissions, the equivalent of over 160 coal-fired power plants for a single year. When commercialized, a single General Fusion power plant will be designed to provide zero-carbon power to approximately 150,000 Canadian homes, with the ability to be placed close to energy demand at a cost competitive with other energy sources such as coal and natural gas.1
Quotes:
“For more than 20 years, General Fusion has advanced its uniquely practical Magnetized Target Fusion technology and IP at its Canadian headquarters. LM26 will significantly de-risk our commercialization program and puts us on track to bring our game-changing, zero-emissions energy solution to Canada, and the world, in the next decade,” said Greg Twinney, CEO, General Fusion.
“Fusion technology has the potential to completely revolutionize the energy sector by giving us access to an affordable unlimited renewable power source. Since General Fusion is at the forefront of this technology, our decision to keep supporting the company will give us the tools we need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reach our climate goals. Our government is proud to invest in this innovative project to drive the creation of hundreds of middle-class jobs and position Canada as a world leader in fusion energy technology,” said The Honourable François-Philippe Champagne, Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry.
“British Columbia has a thriving innovation economy. In August, the B.C. Government announced CA$5 million in provincial support for General Fusion’s homegrown technology, and we’re pleased to see the Federal government has now provided funds to support General Fusion. These investments will help General Fusion as they continue to develop their core technology right here in B.C.,” said Brenda Bailey, B.C. Minister of Jobs, Economic Development and Innovation.
Quick Facts:
*Magnetized Target Fusion uniquely sidesteps challenges to commercialization that other technologies face. The game-changer is a proprietary liquid metal liner in the commercial fusion machine that is mechanically compressed by high-powered pistons. This enables fusion conditions to be created in short pulses rather than creating a sustained reaction. General Fusion’s design does not require large superconducting magnets or an expensive array of lasers.
*LM26 aims to achieve two of the most significant technical milestones required to commercialize fusion energy, targeting fusion conditions of over 100 million degrees Celsius by 2025, and progressing toward scientific breakeven equivalent by 2026.
*LM26’s plasmas will be approximately 50 per cent scale of a commercial fusion machine. It aims to achieve deuterium-tritium breakeven equivalent using deuterium fuel.
*The Canadian government is investing an additional CA$5 million for a total of CA$54.3 million to support the development of General Fusion’s energy technology through the Strategic Innovation Fund program.
*As a result of the government’s ongoing support, General Fusion has advanced its technology, building more than 24 plasma prototypes, filing over 170 patents, and conducting more than 200,000 experiments at its Canadian labs.
This January 11, 2024 General Fusion news release highlights some of the company’s latest research,
General Fusion has published new, peer-reviewed scientific results that validate the company has achieved the smooth, rapid, and symmetric compression of a liquid cavity that is key to the design of a commercial Magnetized Target Fusion power plant. The results, published in one of the foremost scientific journals in fusion, Fusion Engineering and Design [open access paper], validate the performance of General Fusion’s proprietary liquid compression technology for Magnetized Target Fusion and are scalable to a commercial machine.
General Fusion’s Magnetized Target Fusion technology uses mechanical compression of a plasma to achieve fusion conditions. High-speed drivers rapidly power a precisely shaped, symmetrical collapse of a liquid metal cavity that envelopes the plasma. In three years, General Fusion commissioned a prototype of its liquid compression system and completed over 1,000 shots, validating the compression technology. In addition, this scale model of General Fusion’s commercial compression system verified the company’s open-source computational fluid dynamics simulation. The paper confirms General Fusion’s concept for the compression system of a commercial machine.
“General Fusion has proven success scaling individual technologies, creating the pathway to integrate, deploy, and commercialize practical fusion energy,” said Greg Twinney, CEO, General Fusion. “The publication of these results demonstrates General Fusion has the science and engineering capabilities to progress the design of our proprietary liquid compression system to commercialization.”
General Fusion’s approach to compressing plasma to create fusion energy is unique. Its Magnetized Target Fusion technology is designed to address the barriers to commercialization that other fusion technologies still face. The game-changer is the proprietary liquid metal liner in the fusion vessel that is mechanically compressed by high-powered pistons. This allows General Fusion to create fusion conditions in short pulses, rather than creating a sustained reaction, while protecting the machine’s vessel, extracting heat, and re-breeding fuel.
Today [January 11, 2024] at its Canadian labs, General Fusion is building a ground-breaking Magnetized Target Fusion demonstration called Lawson Machine 26 (LM26). Designed to reach fusion conditions of over 100 million degrees Celsius by 2025 and progress towards scientific breakeven equivalent by 2026, LM26 fast-tracks General Fusion’s technical progress to provide commercial fusion energy to the grid by the early to mid-2030s.
Exciting times for us all and I wish good luck to all of the clean energy efforts wherever they are being pursued.