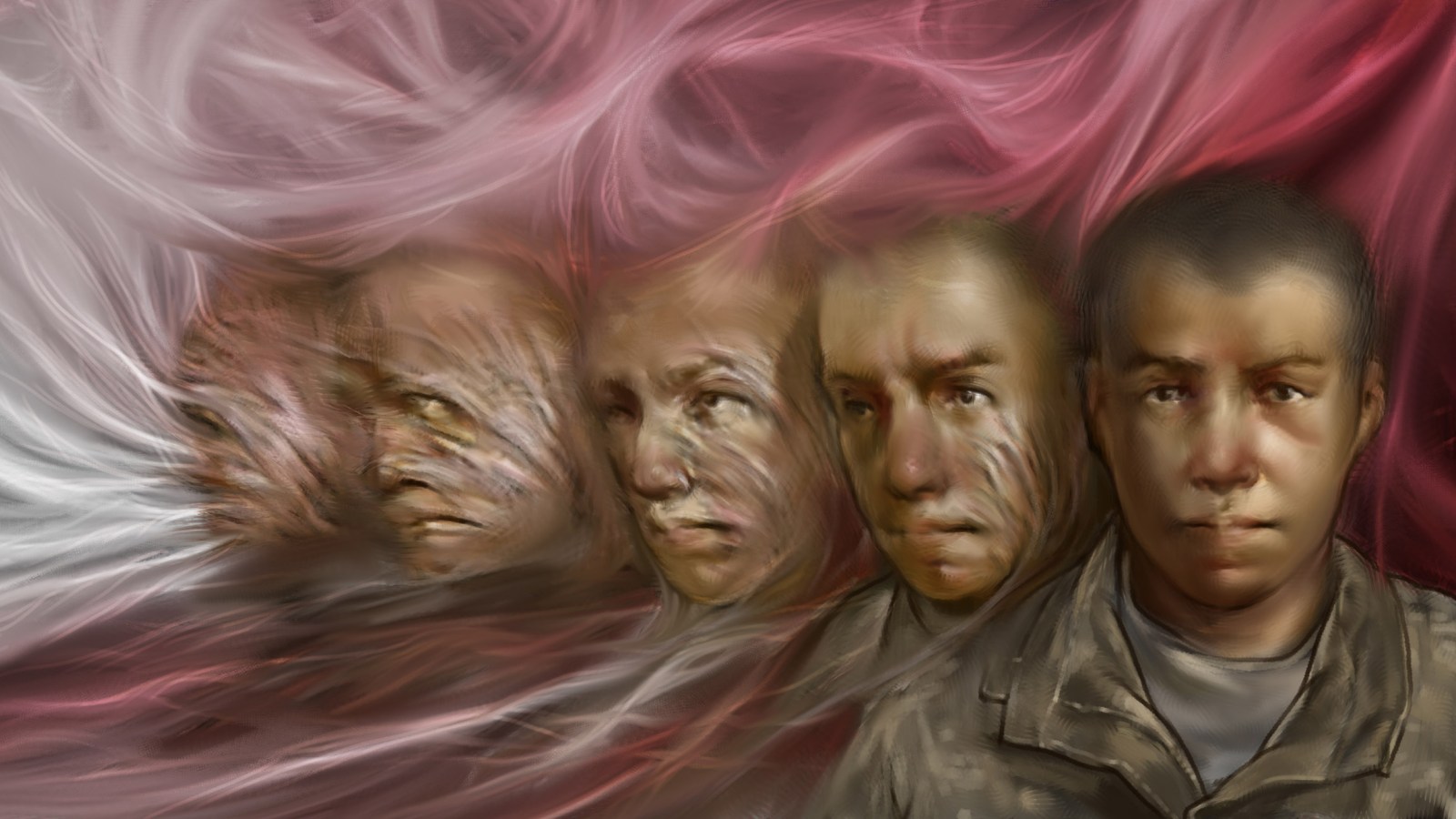
The last time (June 18, 2018 post) I mentioned xenotransplantation (transplanting organs from one species into another species; see more here), it was in the context of an art/sci (or sciart) event coming to Vancouver (Canada).,

Patricia Piccinini’s Curious Imaginings Courtesy: Vancouver Biennale [downloaded from http://dailyhive.com/vancouver/vancouver-biennale-unsual-public-art-2018/]
…
The latest edition of the Vancouver Biennale was featured in a June 6, 2018 news item on the Daily Hive (Vancouver),
…
Melbourne artist Patricia Piccinini’s Curious Imaginings is expected to be one of the most talked about installations of the exhibit. Her style of “oddly captivating, somewhat grotesque, human-animal hybrid creature” is meant to be shocking and thought-provoking.
Piccinini’s interactive [emphasis mine] experience will “challenge us to explore the social impacts of emerging biotechnology and our ethical limits in an age where genetic engineering and digital technologies are already pushing the boundaries of humanity.”
Piccinini’s work will be displayed in the 105-year-old Patricia Hotel in Vancouver’s Strathcona neighbourhood. The 90-day ticketed exhibition [emphasis mine] is scheduled to open this September [2018].
…
(The show opens on Sept. 14, 2018.)
At the time, I had yet to stumble across Ingfei Chen’s thoughtful dive into the topic in her May 9, 2018 article for Slate.com,
In the United States, the clock is ticking for more than 114,700 adults and children waiting for a donated kidney or other lifesaving organ, and each day, nearly 20 of them die. Researchers are devising a new way to grow human organs inside other animals, but the method raises potentially thorny ethical issues. Other conceivable futuristic techniques sound like dystopian science fiction. As we envision an era of regenerative medicine decades from now, how far is society willing to go to solve the organ shortage crisis?
I found myself pondering this question after a discussion about the promises of stem cell technologies veered from the intriguing into the bizarre. I was interviewing bioengineer Zev Gartner, co-director and research coordinator of the Center for Cellular Construction at the University of California, San Francisco, about so-called organoids, tiny clumps of organlike tissue that can self-assemble from human stem cells in a Petri dish. These tissue bits are lending new insights into how our organs form and diseases take root. Some researchers even hope they can nurture organoids into full-size human kidneys, pancreases, and other organs for transplantation.
Certain organoid experiments have recently set off alarm bells, but when I asked Gartner about it, his radar for moral concerns was focused elsewhere. For him, the “really, really thought-provoking” scenarios involve other emerging stem cell–based techniques for engineering replacement organs for people, he told me. “Like blastocyst complementation,” he said.
Never heard of it? Neither had I. Turns out it’s a powerful new genetic engineering trick that researchers hope to use for growing human organs inside pigs or sheep—organs that could be genetically personalized for transplant patients, in theory avoiding immune-system rejection problems. The science still has many years to go, but if it pans out, it could be one solution to the organ shortage crisis. However, the prospect of creating hybrid animals with human parts and killing them to harvest organs has already raised a slew of ethical questions. In 2015, the National Institutes of Health placed a moratorium on federal funding of this nascent research area while it evaluated and discussed the issues.
As Gartner sees it, the debate over blastocyst complementation research—work that he finds promising—is just one of many conversations that society needs to have about the ethical and social costs and benefits of future technologies for making lifesaving transplant organs. “There’s all these weird ways that we could go about doing this,” he said, with a spectrum of imaginable approaches that includes organoids, interspecies organ farming, and building organs from scratch using 3D bioprinters. But even if it turns out we can produce human organs in these novel ways, the bigger issue, in each technological instance, may be whether we should.
Gartner crystallized things with a downright creepy example: “We know that the best bioreactor for tissues and organs for humans are human beings,” he said. Hypothetically, “the best way to get you a new heart would be to clone you, grow up a copy of yourself, and take the heart out.” [emphasis mine] Scientists could probably produce a cloned person with the technologies we already have, if money and ethics were of no concern. “But we don’t want to go there, right?” he added in the next breath. “The ethics involved in doing it are not compatible with who we want to be as a society.”
…
This sounds like Gartner may have been reading some science fiction, specifically, Lois McMaster Bujold and her Barrayar series where she often explored the ethics and possibilities of bioengineering. At this point, some of her work seems eerily prescient.
As for Chen’s article, I strongly encourage you to read it in its entirety if you have the time.
Medicine, healing, and big money
At about the same time, there was a May 31, 2018 news item on phys.org offering a perspective from some of the leaders in the science and the business (Note: Links have been removed),
Over the past few years, researchers led by George Church have made important strides toward engineering the genomes of pigs to make their cells compatible with the human body. So many think that it’s possible that, with the help of CRISPR technology, a healthy heart for a patient in desperate need might one day come from a pig.
“It’s relatively feasible to change one gene in a pig, but to change many dozens—which is quite clear is the minimum here—benefits from CRISPR,” an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats, said Church, the Robert Winthrop Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School (HMS) and a core faculty member of Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering. Xenotransplantation is “one of few” big challenges (along with gene drives and de-extinction, he said) “that really requires the ‘oomph’ of CRISPR.”
To facilitate the development of safe and effective cells, tissues, and organs for future medical transplantation into human patients, Harvard’s Office of Technology Development has granted a technology license to the Cambridge biotech startup eGenesis.
Co-founded by Church and former HMS doctoral student Luhan Yang in 2015, eGenesis announced last year that it had raised $38 million to advance its research and development work. At least eight former members of the Church lab—interns, doctoral students, postdocs, and visiting researchers—have continued their scientific careers as employees there.
“The Church Lab is well known for its relentless pursuit of scientific achievements so ambitious they seem improbable—and, indeed, [for] its track record of success,” said Isaac Kohlberg, Harvard’s chief technology development officer and senior associate provost. “George deserves recognition too for his ability to inspire passion and cultivate a strong entrepreneurial drive among his talented research team.”
The license from Harvard OTD covers a powerful set of genome-engineering technologies developed at HMS and the Wyss Institute, including access to foundational intellectual property relating to the Church Lab’s 2012 breakthrough use of CRISPR, led by Yang and Prashant Mali, to edit the genome of human cells. Subsequent innovations that enabled efficient and accurate editing of numerous genes simultaneously are also included. The license is exclusive to eGenesis but limited to the field of xenotransplantation.
A May 30, 2018 Harvard University news release by Caroline Petty, which originated the news item, explores some of the issues associated with incubating humans organs in other species,
The prospect of using living, nonhuman organs, and concerns over the infectiousness of pathogens either present in the tissues or possibly formed in combination with human genetic material, have prompted the Food and Drug Administration to issue detailed guidance on xenotransplantation research and development since the mid-1990s. In pigs, a primary concern has been that porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs), strands of potentially pathogenic DNA in the animals’ genomes, might infect human patients and eventually cause disease. [emphases mine]
That’s where the Church lab’s CRISPR expertise has enabled significant advances. In 2015, the lab published important results in the journal Science, successfully demonstrating the use of genome engineering to eliminate all 62 PERVs in porcine cells. Science later called it “the most widespread CRISPR editing feat to date.”
In 2017, with collaborators at Harvard, other universities, and eGenesis, Church and Yang went further. Publishing again in Science, they first confirmed earlier researchers’ fears: Porcine cells can, in fact, transmit PERVs into human cells, and those human cells can pass them on to other, unexposed human cells. (It is still unknown under what circumstances those PERVs might cause disease.) In the same paper, they corrected the problem, announcing the embryogenesis and birth of 37 PERV-free pigs. [Note: My July 17, 2018 post features research which suggests CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing may cause greater genetic damage than had been thought.]
“Taken together, those innovations were stunning,” said Vivian Berlin, director of business development in OTD, who manages the commercialization strategy for much of Harvard’s intellectual property in the life sciences. “That was the foundation they needed, to convince both the scientific community and the investment community that xenotransplantation might become a reality.”
“After hundreds of tests, this was a critical milestone for eGenesis — and the entire field — and represented a key step toward safe organ transplantation from pigs,” said Julie Sunderland, interim CEO of eGenesis. “Building on this study, we hope to continue to advance the science and potential of making xenotransplantation a safe and routine medical procedure.”
It’s not, however, the end of the story: An immunological challenge remains, which eGenesis will need to address. The potential for a patient’s body to outright reject transplanted tissue has stymied many previous attempts at xenotransplantation. Church said numerous genetic changes must be achieved to make porcine organs fully compatible with human patients. Among these are edits to several immune functions, coagulation functions, complements, and sugars, as well as the PERVs.
“Trying the straight transplant failed almost immediately, within hours, because there’s a huge mismatch in the carbohydrates on the surface of the cells, in particular alpha-1-3-galactose, and so that was a showstopper,” Church explained. “When you delete that gene, which you can do with conventional methods, you still get pretty fast rejection, because there are a lot of other aspects that are incompatible. You have to take care of each of them, and not all of them are just about removing things — some of them you have to humanize. There’s a great deal of subtlety involved so that you get normal pig embryogenesis but not rejection.
“Putting it all together into one package is challenging,” he concluded.
In short, it’s the next big challenge for CRISPR.
Not unexpectedly, there is no mention of the CRISPR patent fight between Harvard/MIT’s (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Broad Institute and the University of California at Berkeley (UC Berkeley). My March 15, 2017 posting featured an outcome where the Broad Institute won the first round of the fight. As I recall, it was a decision based on the principles associated with King Solomon, i.e., the US Patent Office, divided the baby and UCBerkeley got the less important part of the baby. As you might expect the decision has been appealed. In an April 30, 2018 piece, Scientific American reprinted an article about the latest round in the fight written by Sharon Begley for STAT (Note: Links have been removed),
All You Need to Know for Round 2 of the CRISPR Patent Fight
It’s baaaaack, that reputation-shredding, stock-moving fight to the death over key CRISPR patents. On Monday morning in Washington, D.C., the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit will hear oral arguments in University of California v. Broad Institute. Questions?
How did we get here? The patent office ruled in February 2017 that the Broad’s 2014 CRISPR patent on using CRISPR-Cas9 to edit genomes, based on discoveries by Feng Zhang, did not “interfere” with a patent application by UC based on the work of UC Berkeley’s Jennifer Doudna. In plain English, that meant the Broad’s patent, on using CRISPR-Cas9 to edit genomes in eukaryotic cells (all animals and plants, but not bacteria), was different from UC’s, which described Doudna’s experiments using CRISPR-Cas9 to edit DNA in a test tube—and it was therefore valid. The Patent Trial and Appeal Board concluded that when Zhang got CRISPR-Cas9 to work in human and mouse cells in 2012, it was not an obvious extension of Doudna’s earlier research, and that he had no “reasonable expectation of success.” UC appealed, and here we are.
…
For anyone who may not realize what the stakes are for these institutions, Linda Williams in a March 16, 1999 article for the LA Times had this to say about universities, patents, and money,
The University of Florida made about $2 million last year in royalties on a patent for Gatorade Thirst Quencher, a sports drink that generates some $500 million to $600 million a year in revenue for Quaker Oats Co.
The payments place the university among the top five in the nation in income from patent royalties.
Oh, but if some people on the Gainesville, Fla., campus could just turn back the clock. “If we had done Gatorade right, we would be getting $5 or $6 million (a year),” laments Donald Price, director of the university’s office of corporate programs. “It is a classic example of how not to handle a patent idea,” he added.
Gatorade was developed in 1965 when many universities were ill equipped to judge the commercial potential of ideas emerging from their research labs. Officials blew the university’s chance to control the Gatorade royalties when they declined to develop a professor’s idea.
…
The Gatorade story does not stop there and, even though it’s almost 20 years old, this article stands the test of time. I strongly encourage you to read it if the business end of patents and academia interest you or if you would like to develop more insight into the Broad Institute/UC Berkeley situation.
Getting back to the science, there is that pesky matter of diseases crossing over from one species to another. While, Harvard and eGenesis claim a victory in this area, it seems more work needs to be done.
Infections from pigs
An August 29, 2018 University of Alabama at Birmingham news release (also on EurekAlert) by Jeff Hansen, describes the latest chapter in the quest to provide more organs for transplantion,
A shortage of organs for transplantation — including kidneys and hearts — means that many patients die while still on waiting lists. So, research at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and other sites has turned to pig organs as an alternative. [emphasis mine]
Using gene-editing, researchers have modified such organs to prevent rejection, and research with primates shows the modified pig organs are well-tolerated.
An added step is needed to ensure the safety of these inter-species transplants — sensitive, quantitative assays for viruses and other infectious microorganisms in donor pigs that potentially could gain access to humans during transplantation.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration requires such testing, prior to implantation, of tissues used for xenotransplantation from animals to humans. It is possible — though very unlikely — that an infectious agent in transplanted tissues could become an emerging infectious disease in humans.
In a paper published in Xenotransplantation, Mark Prichard, Ph.D., and colleagues at UAB have described the development and testing of 30 quantitative assays for pig infectious agents. These assays had sensitivities similar to clinical lab assays for viral loads in human patients. After validation, the UAB team also used the assays on nine sows and 22 piglets delivered from the sows through caesarian section.
“Going forward, ensuring the safety of these organs is of paramount importance,” Prichard said. “The use of highly sensitive techniques to detect potential pathogens will help to minimize adverse events in xenotransplantation.”
“The assays hold promise as part of the screening program to identify suitable donor animals, validate and release transplantable organs for research purposes, and monitor transplant recipients,” said Prichard, a professor in the UAB Department of Pediatrics and director of the Department of Pediatrics Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory.
The UAB researchers developed quantitative polymerase chain reaction, or qPCR, assays for 28 viruses sometimes found in pigs and two groups of mycoplasmas. They established reproducibility, sensitivity, specificity and lower limit of detection for each assay. All but three showed features of good quantitative assays, and the lower limit of detection values ranged between one and 16 copies of the viral or bacterial genetic material.
Also, the pig virus assays did not give false positives for some closely related human viruses.
As a start to understanding the infectious disease load in normal healthy animals and ensuring the safety of pig tissues used in xenotransplantation research, the researchers then screened blood, nasal swab and stool specimens from nine adult sows and 22 of their piglets delivered by caesarian section.
Mycoplasma species and two distinct herpesviruses were the most commonly detected microorganisms. Yet 14 piglets that were delivered from three sows infected with either or both herpesviruses were not infected with the herpesviruses, showing that transmission of these viruses from sow to the caesarian-delivery piglet was inefficient.
Prichard says the assays promise to enhance the safety of pig tissues for xenotransplantation, and they will also aid evaluation of human specimens after xenotransplantation.
The UAB researchers say they subsequently have evaluated more than 300 additional specimens, and that resulted in the detection of most of the targets. “The detection of these targets in pig specimens provides reassurance that the analytical methods are functioning as designed,” said Prichard, “and there is no a priori reason some targets might be more difficult to detect than others with the methods described here.”
As is my custom, here’s a link to and a citation for the paper,
Xenotransplantation panel for the detection of infectious agents in pigs by Caroll B. Hartline, Ra’Shun L. Conner, Scott H. James, Jennifer Potter, Edward Gray, Jose Estrada, Mathew Tector, A. Joseph Tector, Mark N. Prichard. Xenotransplantaion Volume 25, Issue 4 July/August 2018 e12427 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/xen.12427 First published: 18 August 2018
This paper is open access.
All this leads to questions about chimeras. If a pig is incubating organs with human cells it’s a chimera but then means the human receiving the organ becomes a chimera too. (For an example, see my Dec. 22, 2013 posting where there’s mention of a woman who received a trachea from a pig. Scroll down about 30% of the way.)
What is it to be human?
A question much beloved of philosophers and others, the question seems particularly timely with xenotransplantion and other developments such neuroprosthetics (cyborgs) and neuromorphic computing (brainlike computing).
As I’ve noted before, although not recently, popular culture offers a discourse on these issues. Take a look at the superhero movies and the way in which enhanced humans and aliens are presented. For example, X-Men comics and movies present mutants (humans with enhanced abilities) as despised and rejected. Video games (not really my thing but there is the Deus Ex series which has as its hero, a cyborg also offer insight into these issues.
Other than popular culture and in the ‘bleeding edge’ arts community, I can’t recall any public discussion on these matters arising from the extraordinary set of technologies which are being deployed or prepared for deployment in the foreseeable future.
(If you’re in Vancouver (Canada) from September 14 – December 15, 2018, you may want to check out Piccinini’s work. Also, there’s ” NCSU [North Carolina State University] Libraries, NC State’s Genetic Engineering and Society (GES) Center, and the Gregg Museum of Art & Design have issued a public call for art for the upcoming exhibition Art’s Work in the Age of Biotechnology: Shaping our Genetic Futures.” from my Sept. 6, 2018 posting. Deadline: Oct. 1, 2018.)
At a guess, there will be pushback from people who have no interest in debating what it is to be human as they already know, and will find these developments, when they learn about them, to be horrifying and unnatural.